High-Sensitivity Flow Cytometric Detection of a Small Circulating Population of Nodal T-Follicular Helper Cell Lymphoma Angioimmunoblastic Type Cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc5114Keywords:
Nodal T-follicular helper cell lymphoma angioimmunoblastic type, Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma, Peripheral blood involvement, Flow cytometryAbstract
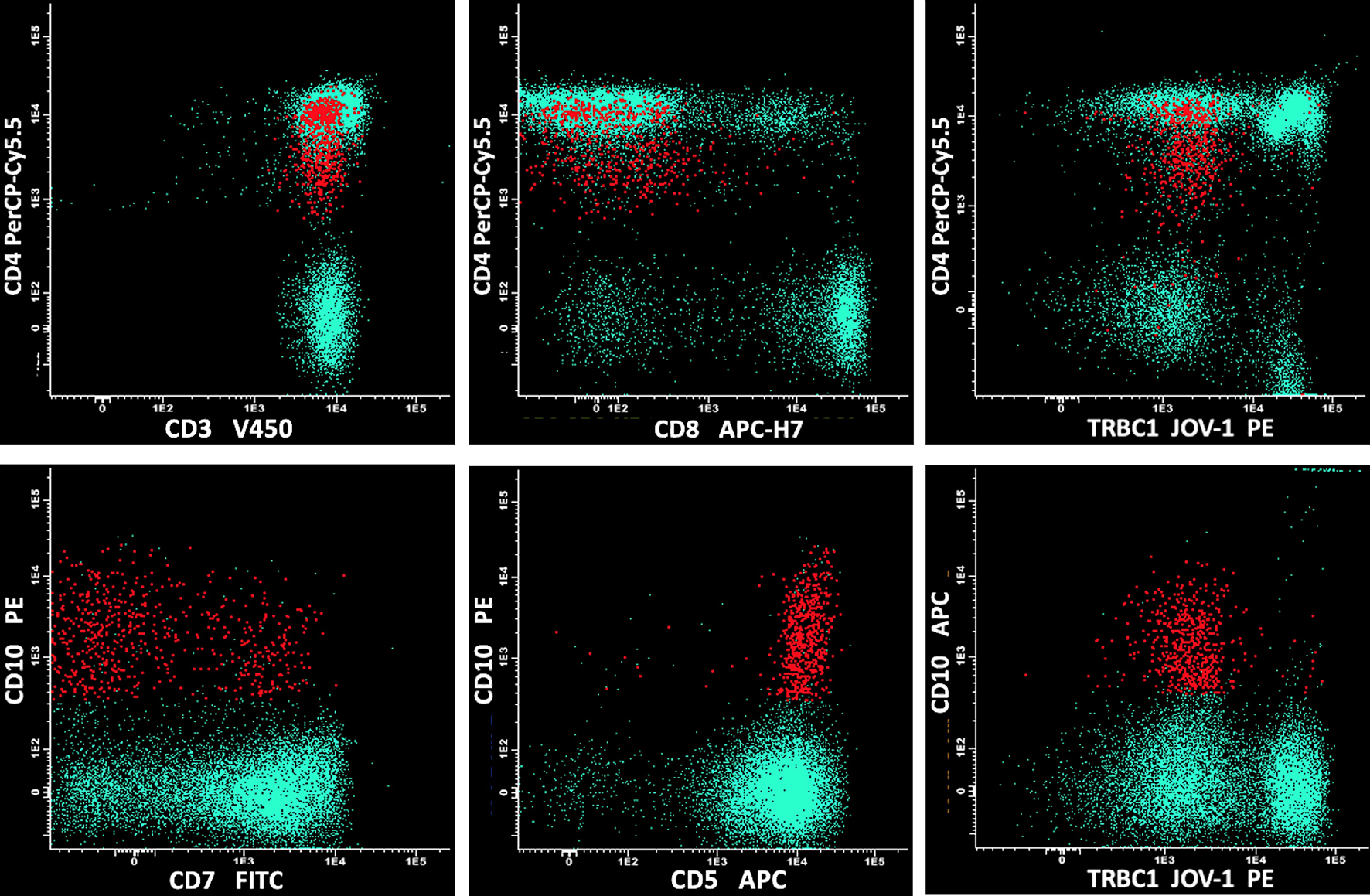
Nodal T-follicular helper cell lymphoma angioimmunoblastic type (nTFHL-AI) is a rare and aggressive neoplasm of mature T-follicular helper cells. nTFHL-AI is characterized by polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia, hemolytic anemia, circulating immune complexes, and cold agglutinins. nTFHL-AI is also often associated with B-cell or plasma cell expansion, mimicking B-cell lymphomas or plasma cell neoplasms. Therefore, the diagnosis of nTFHL-AI can sometimes be challenging and requires a specific immunophenotypic panel. However, the peripheral blood involvement in nTFHL-AI seems rare and has not been frequently addressed in the literature. We report the case of a 54-year-old man with multiple lymphadenopathies, hepatosplenomegaly, and skin rash, complaining of asthenia. Peripheral blood smear showed plasmacytoid cells and red cell rouleaux. A first flow cytometry screening panel of peripheral blood disclosed marked polyclonal plasmacytosis (12%). No mature B lymphocytes were detectable. In the suspicion of an nTFHL-AI, another flow cytometric panel was performed, including CD3, CD4, CD5, CD7, CD8, and CD10. The high-sensitivity flow cytometry analysis disclosed a small circulating population of atypical T cells (0.07%) expressing CD4+, CD3+, CD5+, CD10+, partially CD7+, and negative for CD8. Moreover, anti-TCRβ-chain constant region 1 (TRBC1) antibody (JOVI-1) was used to confirm the T-cell clonal restriction of this abnormal population. Immunohistochemistry on excised lymph node sections was carried out and confirmed the diagnosis of nTFHL-AI. In this case, the unexpected detection of a small circulating population of nTFHL-AI cells by high-sensitivity flow cytometry has prompted an extensive diagnostic workup leading rapidly to the correct diagnosis.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









