Pulmonary Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma and Tuberculosis: A Rare Association With Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc5256Keywords:
Pulmonary MALT lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Diagnosis, ManagementAbstract
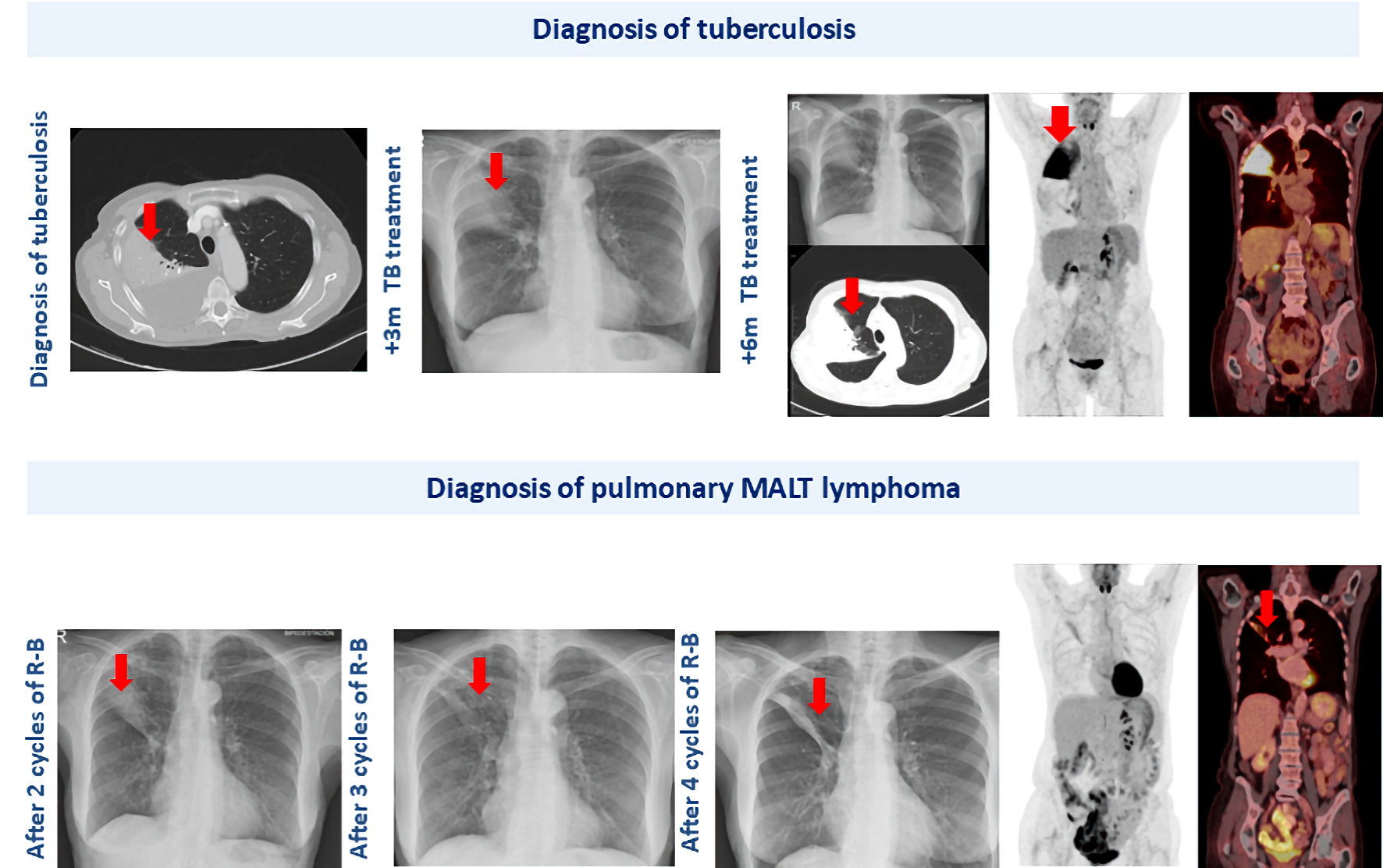
This case report describes the rare coexistence of pulmonary tuberculosis and pulmonary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma in a 68-year-old woman. The initial diagnosis of tuberculosis was supported by clinical, radiological, and microbiological findings, and the patient started on standard tuberculostatic therapy. However, the persistence of radiological abnormalities after several months of appropriate treatment, despite improvement in pleural effusion, raised suspicion for an underlying malignancy. Subsequent imaging and histopathological evaluation confirmed the diagnosis of primary pulmonary MALT lymphoma. The patient was successfully treated with immunochemotherapy, achieving complete remission. This case underscores the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion for alternative or concomitant diagnoses, particularly malignancies, when tuberculosis exhibits an atypical clinical course or when radiological findings fail to resolve as expected. Furthermore, it highlights the need for thorough diagnostic evaluation in patients with persistent pulmonary abnormalities to ensure timely and accurate diagnosis and management.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









