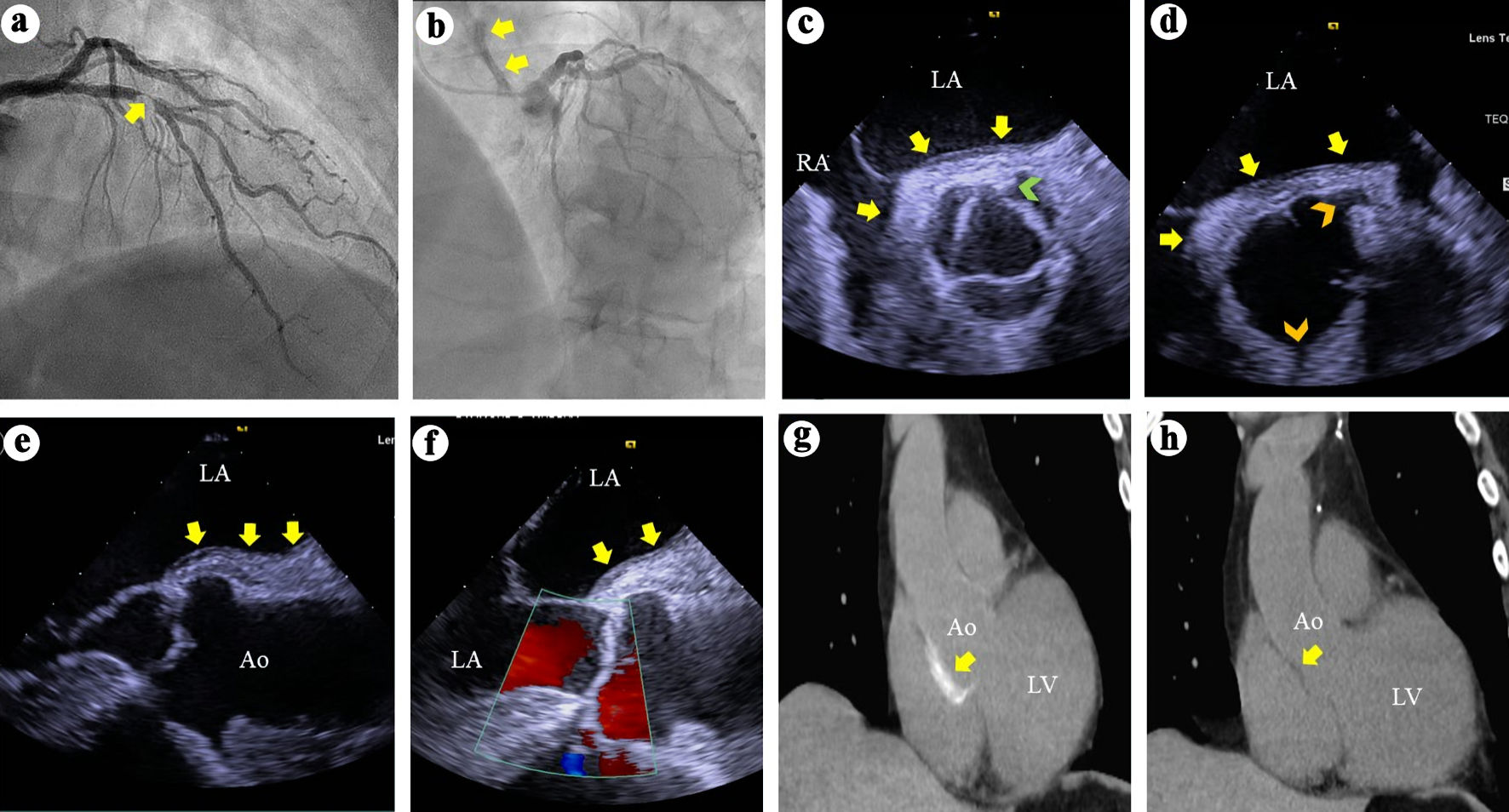
Figure 1. (a) Right anterior oblique view of the left coronary arteries angiography demonstrates a > 95% complex stenosis (arrow) of the left anterior descending coronary artery. (b) Left anterior and cranial view of the left coronary system demonstrates contrast hang-up or staining (arrows) on the aortic root and ascending aorta. (c) TEE short axis views at the aortic valve level during systole demonstrates soft tissue echo-reflectant thickening of the aortic root posterior wall with medial and lateral extensions (arrows) and a possible small intimal tear (green arrowhead). (d) TEE short-axis view of the aortic root during diastole demonstrates aortic wall thickening (arrows) and intact ostial left main and right coronary arteries (top and bottom arrowheads, respectively). (e, f) TEE long-axis views demonstrate soft tissue thickening of the posterior aortic root and ascending aortic wall (arrows) and intact aortic valve with no regurgitation. (g) Thoracic CT demonstrates contrast uptake at the aortic root and part of the ascending aorta (arrow). (h) Repeat thoracic CT 7 weeks later demonstrates resolution of the contrast uptake at the aortic root and ascending aorta. TEE: transesophageal echocardiography; CT: computed tomography; LA: left atrium; RA: right atrium; Ao: aorta; LV: left ventricle.