Figures
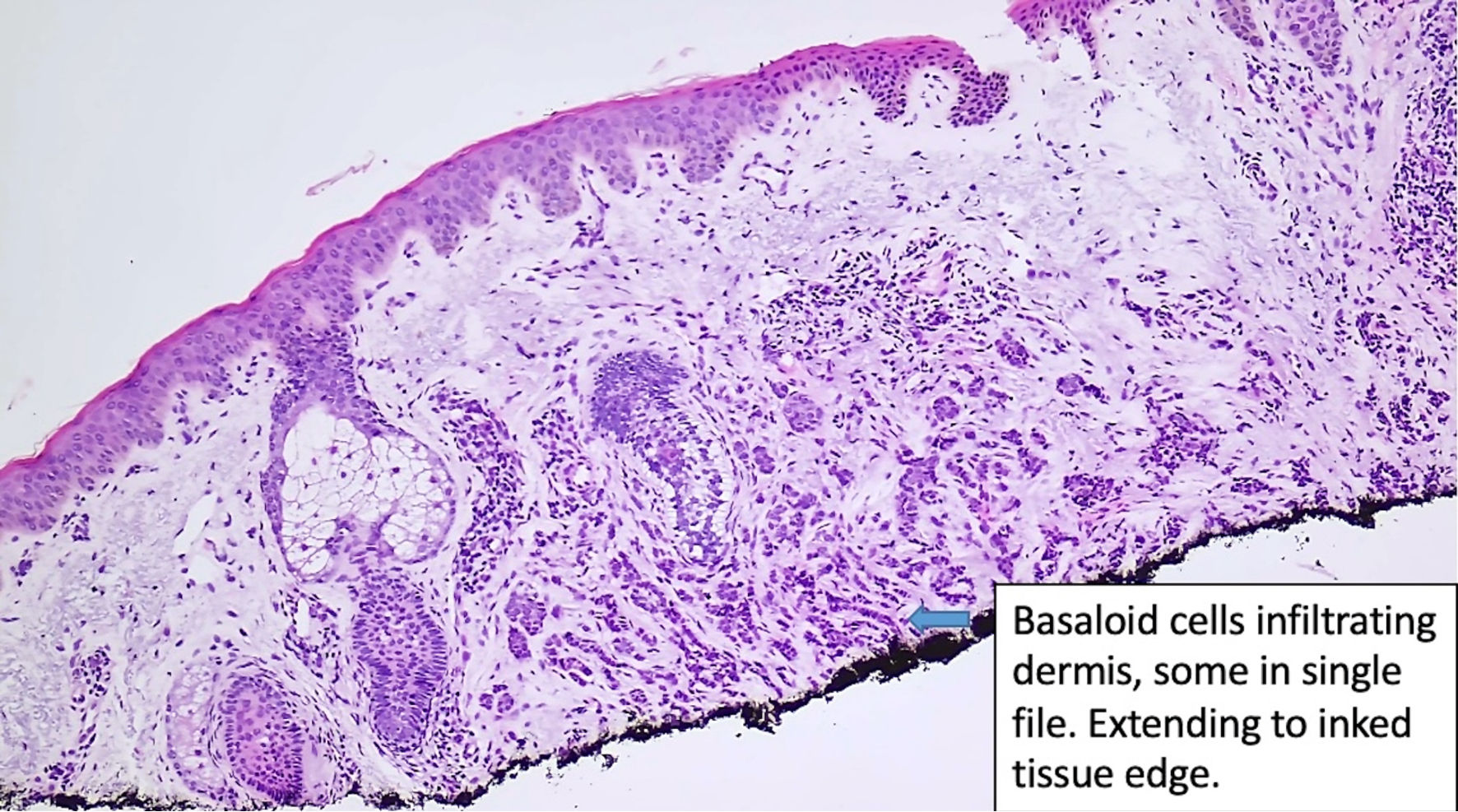
Figure 1. Histologic features of eccrine carcinoma at the initial diagnosis. Basaloid cells are infiltrating the dermis. (original magnification × 100).
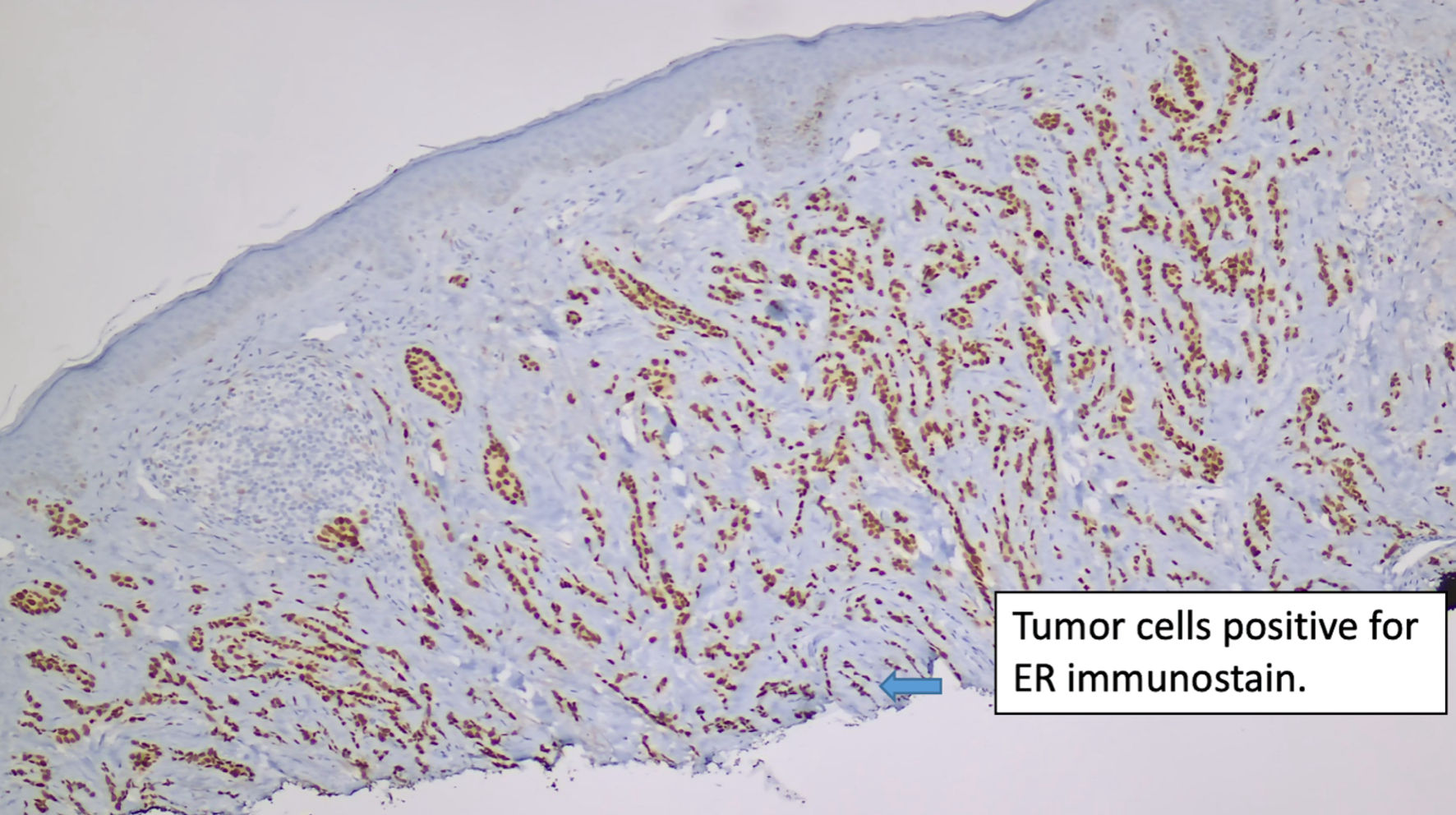
Figure 2. Immunostain for ER (original magnification × 100). ER: estrogen receptor.
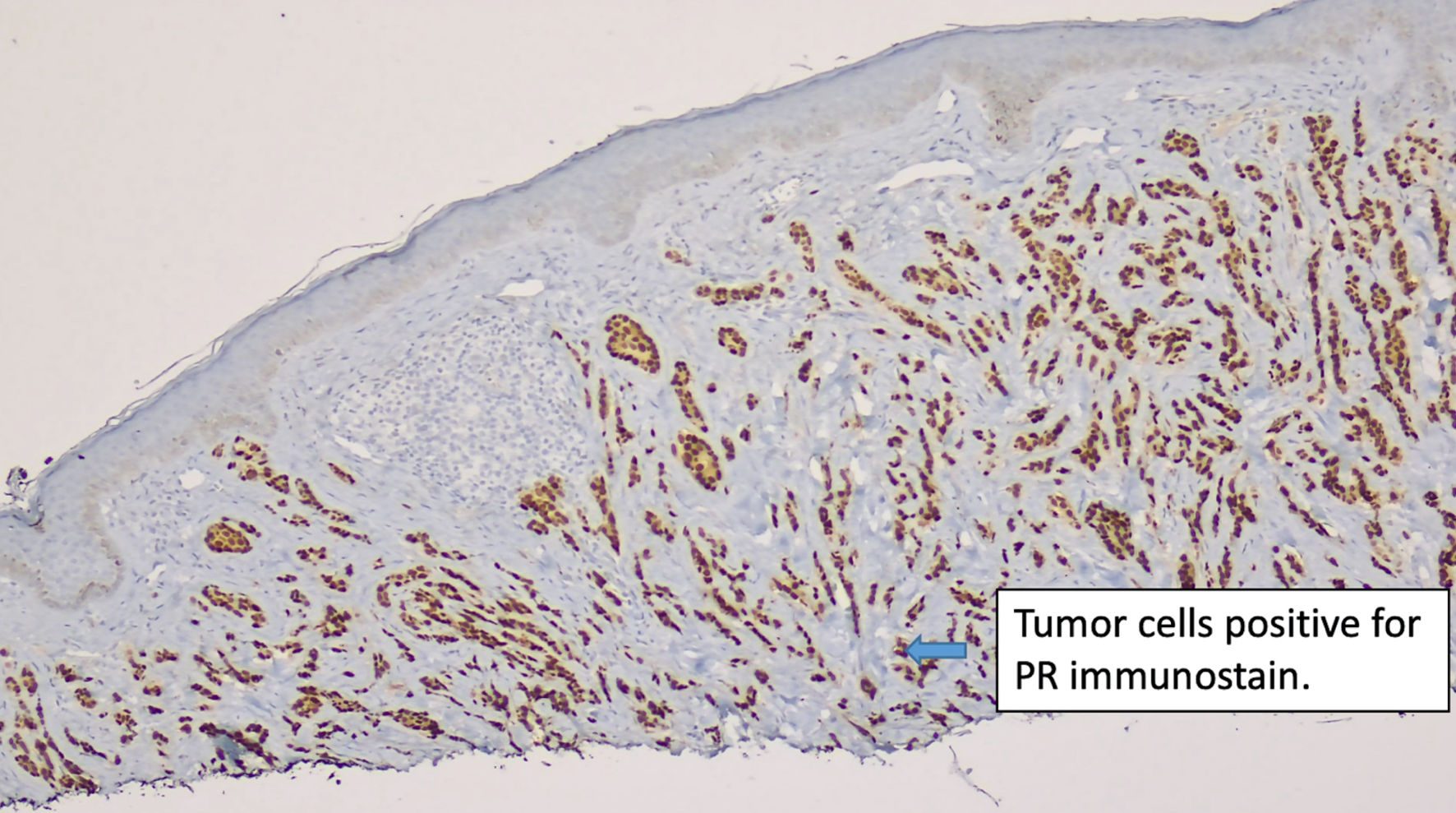
Figure 3. Immunostain for PR (original magnification × 100). PR: progesterone receptor.
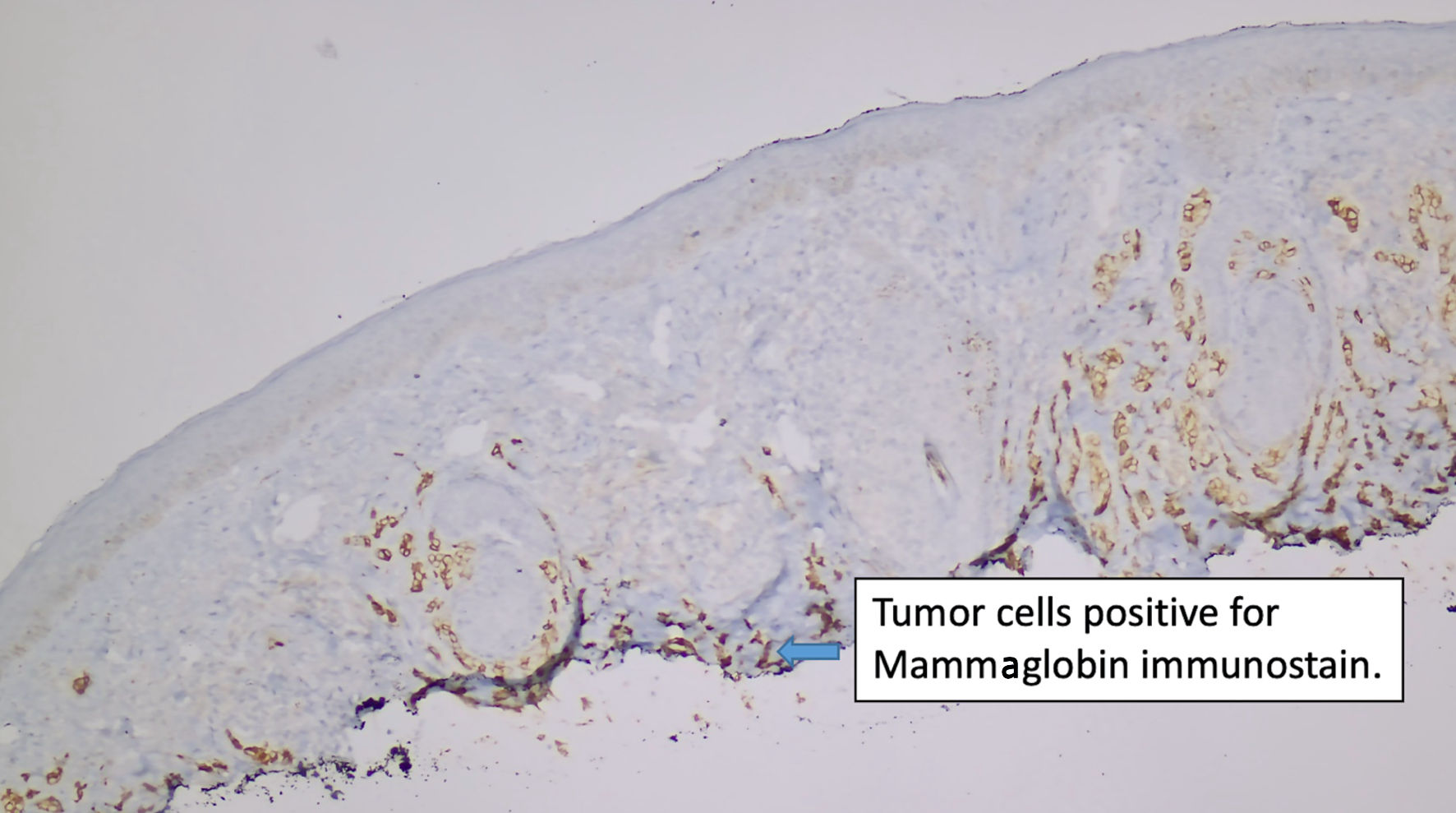
Figure 4. Immunostain for mammaglobin (original magnification × 100).
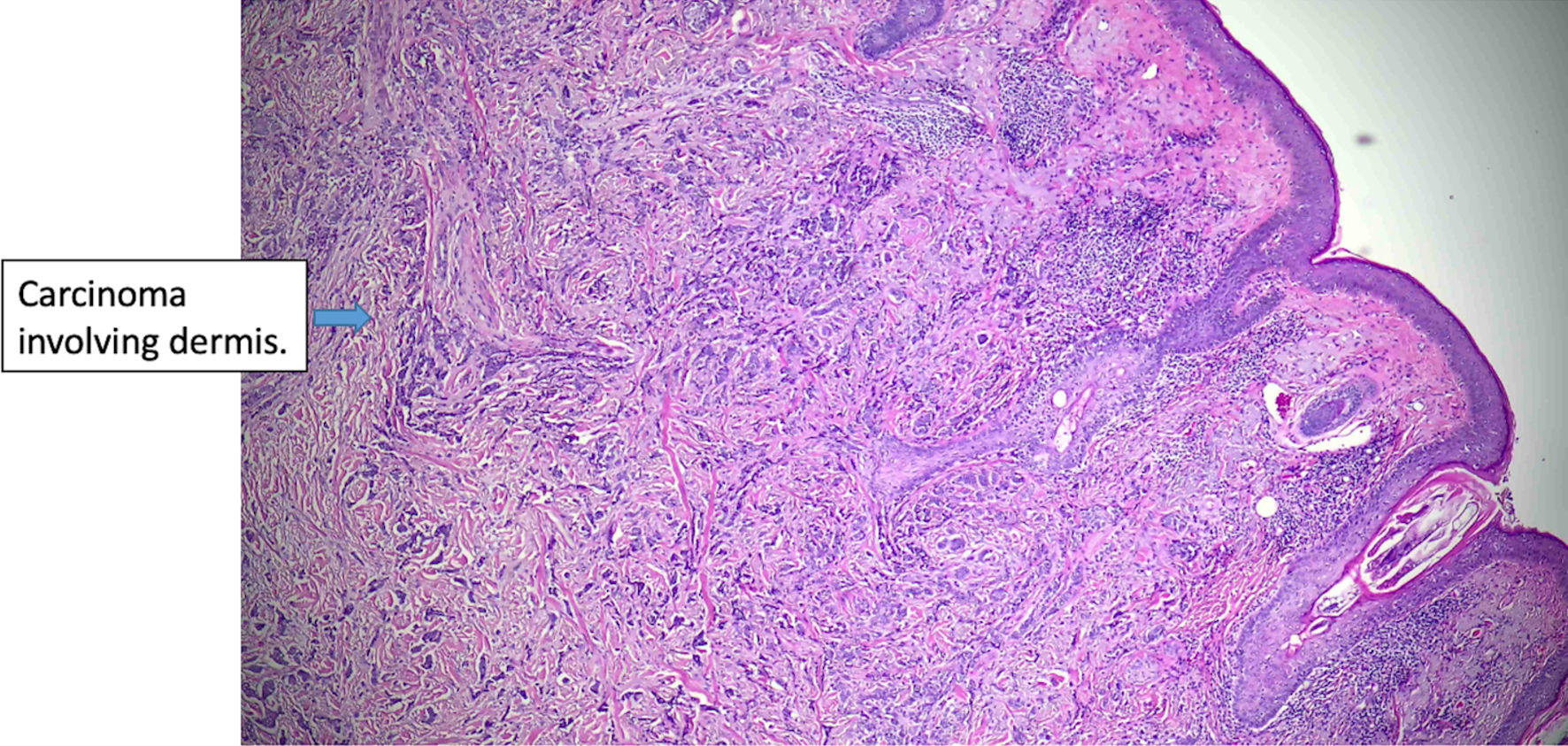
Figure 5. Histologic features of eccrine cell carcinoma at excision. The carcinoma is infiltrative, largely involving the dermis (original magnification × 50).
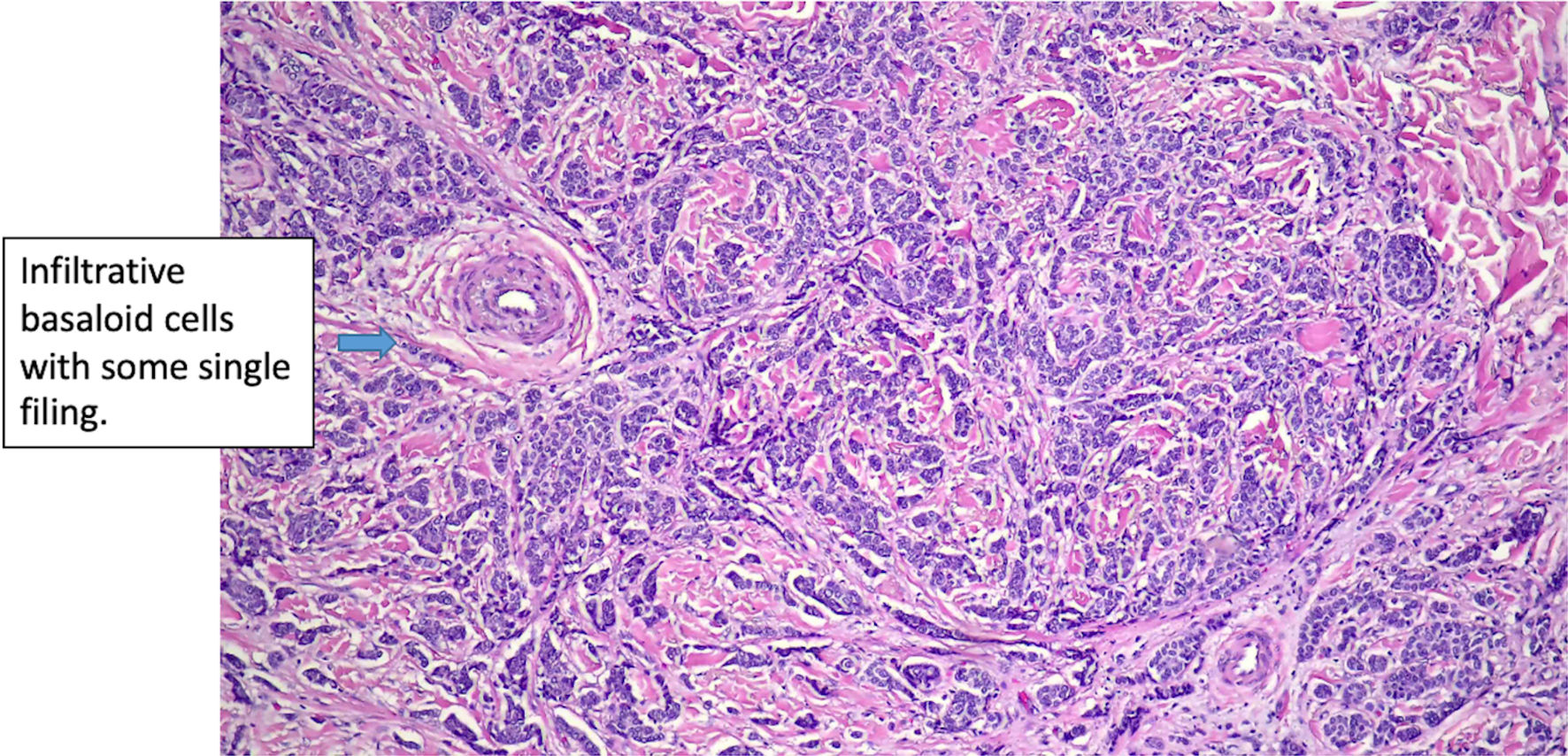
Figure 6. Histologic features of eccrine cell carcinoma at excision. (original magnification × 200).
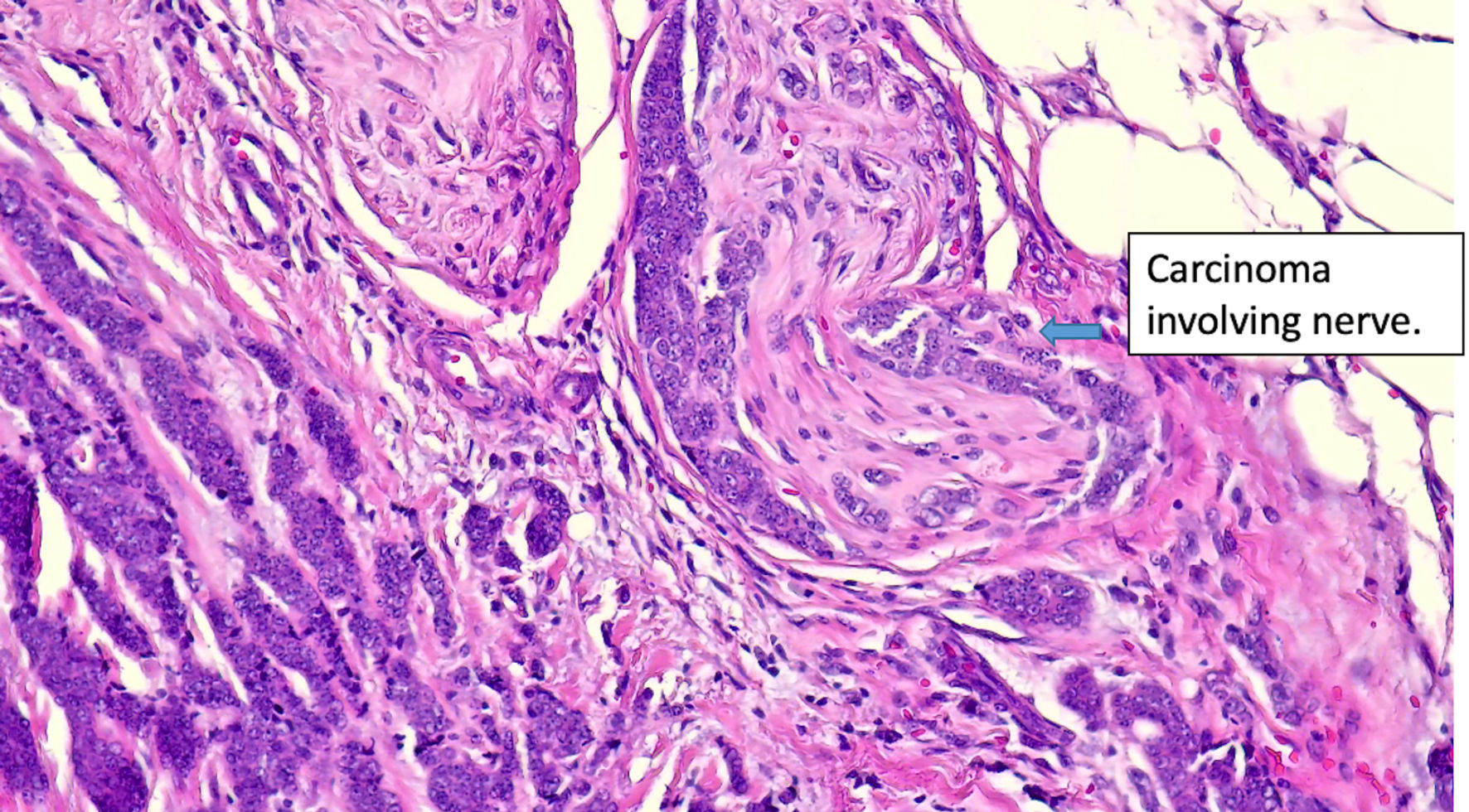
Figure 7. Histologic features of eccrine cell carcinoma at excision. Extensive perineural invasion. (original magnification × 400).
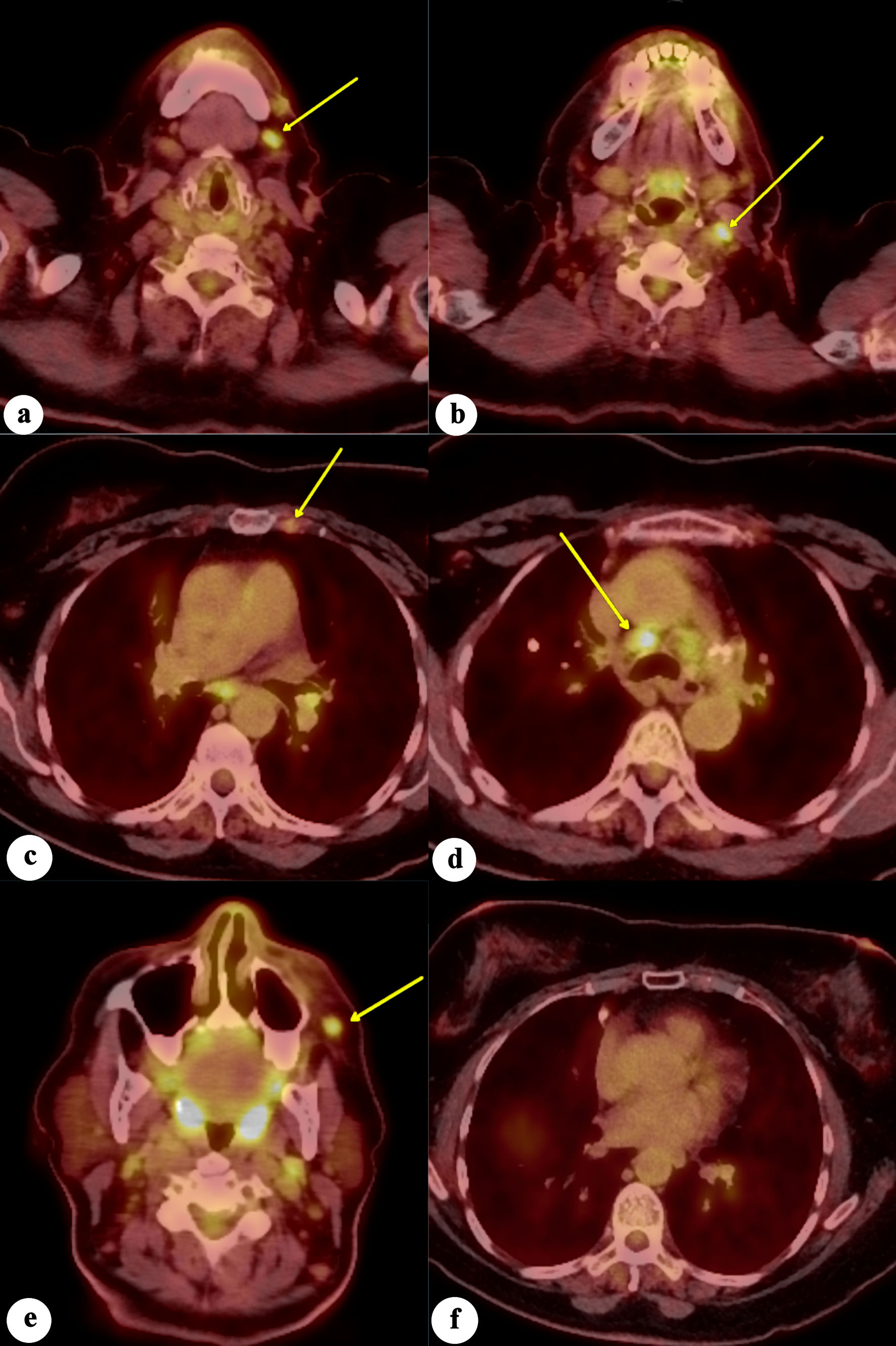
Figure 8. Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) scan of the whole body demonstrates increased FDG avidity in (a) left level 1 lymph node, (b) left level 2 lymph node, (c) left internal mammary lymph node, (d) mediastinal/paratracheal lymph node, and (e) left malar soft-tissue nodule (yellow arrows), concerning for metastatic disease. (f) No evidence of increased FDG avidity within the breast tissues to suggest neoplastic disease.








