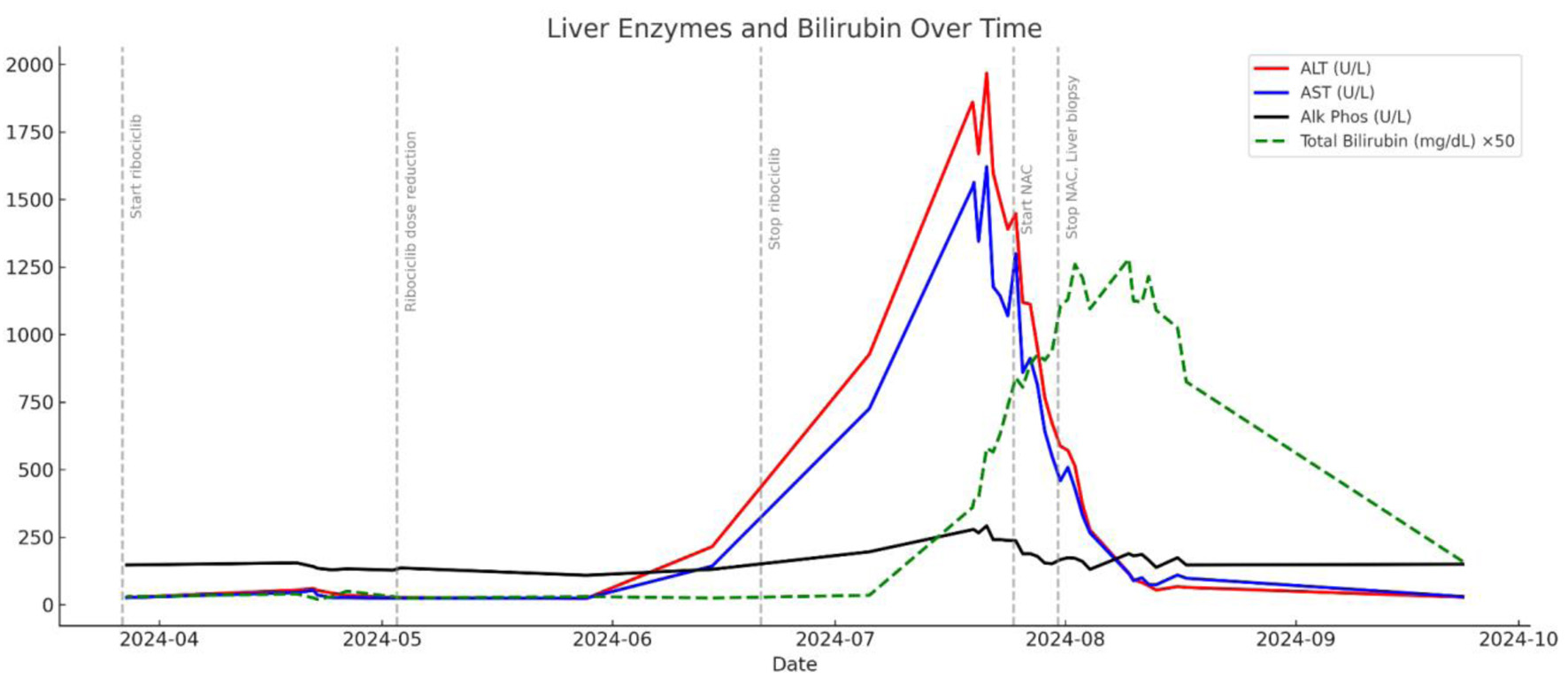
| R-factor | Classify type of liver injury (hepatocellular vs. cholestatic vs. mixed) | R = (ALT ÷ ALT ULN) ÷ (ALP ÷ ALP ULN); ALT = 1,825 U/L (ULN = 40), ALP = 278 U/L (ULN = 120) | R = (1,825/40) ÷ (278/120) = 20.73 | Hepatocellular injury (R ≥ 5) | Confirms hepatocellular pattern, consistent with biopsy findings |
| RUCAM score | Estimate likelihood of drug causality in DILI | Temporal relationship, risk factors, exclusion of alternative causes, dechallenge, known hepatotoxicity, rechallenge | Components (approx): +2 (onset); +3 (dechallenge); +2 (no alt causes); +2 (known hepatotoxin); +1 (female); Total: ∼ 10 | Highly probable (≥ 9) | Strongly supports ribociclib as cause of liver injury |
| Naranjo algorithm | General tool to estimate probability of ADR | Includes timing, prior reports, dechallenge, rechallenge, alternative causes | Components (approx): +2 (timing); +1 (dechallenge); +1 (prior reports); +2 (no alt cause); +1 (biopsy); Total: ∼ 7 | Probable ADR (5 - 8) | Supports ribociclib as likely cause of DILI |