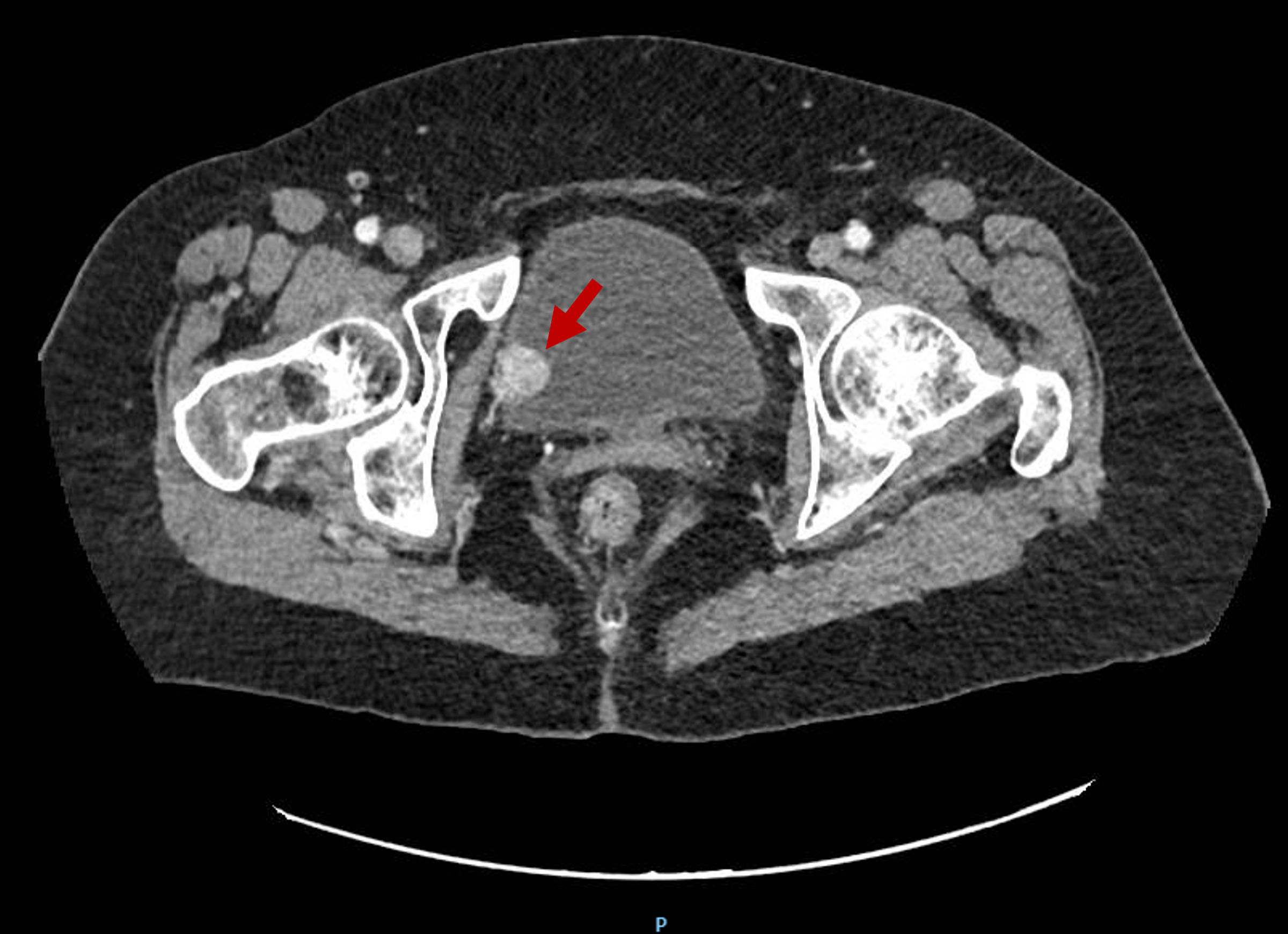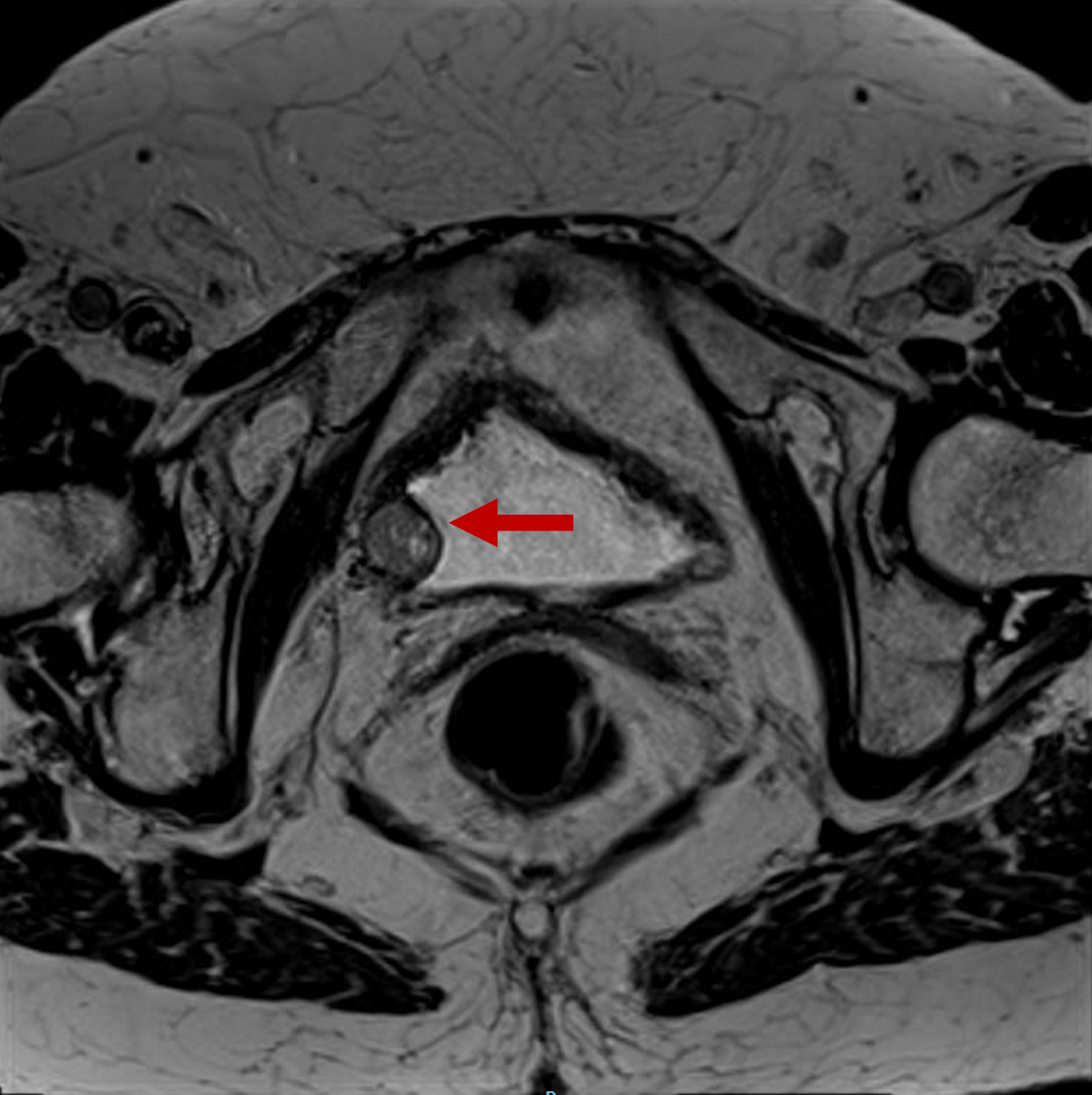
Figure 2. Bladder MRI requested to study the lesion found in the CT scan and ultrasound. The red arrow points to a solid tumor of nodular morphology of 15-mm depending on the right posterolateral margin of the bladder. It shows well-defined contours with no signs of intraluminal extension or regional fat involvement. MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; CT: computed tomography.
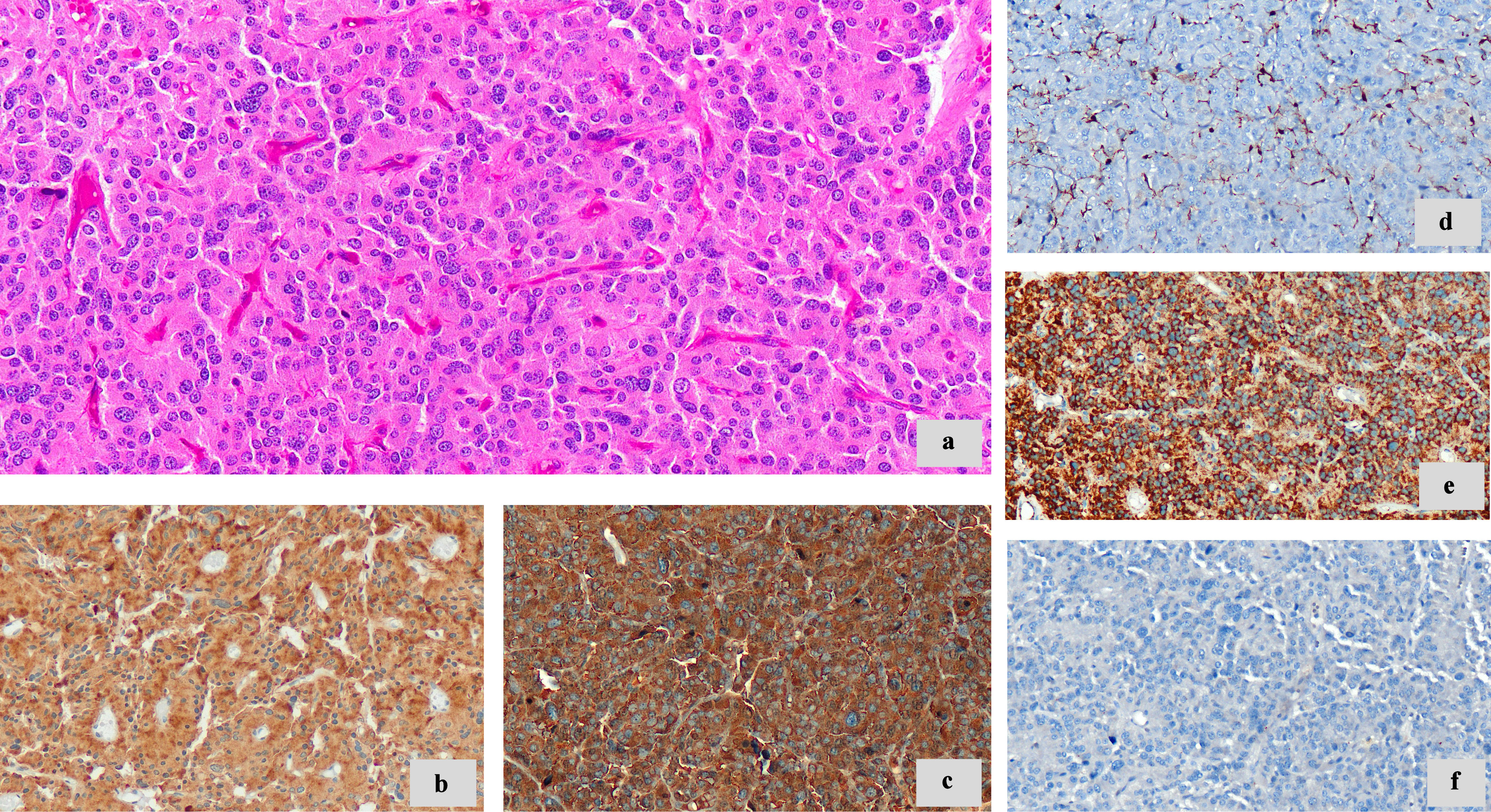
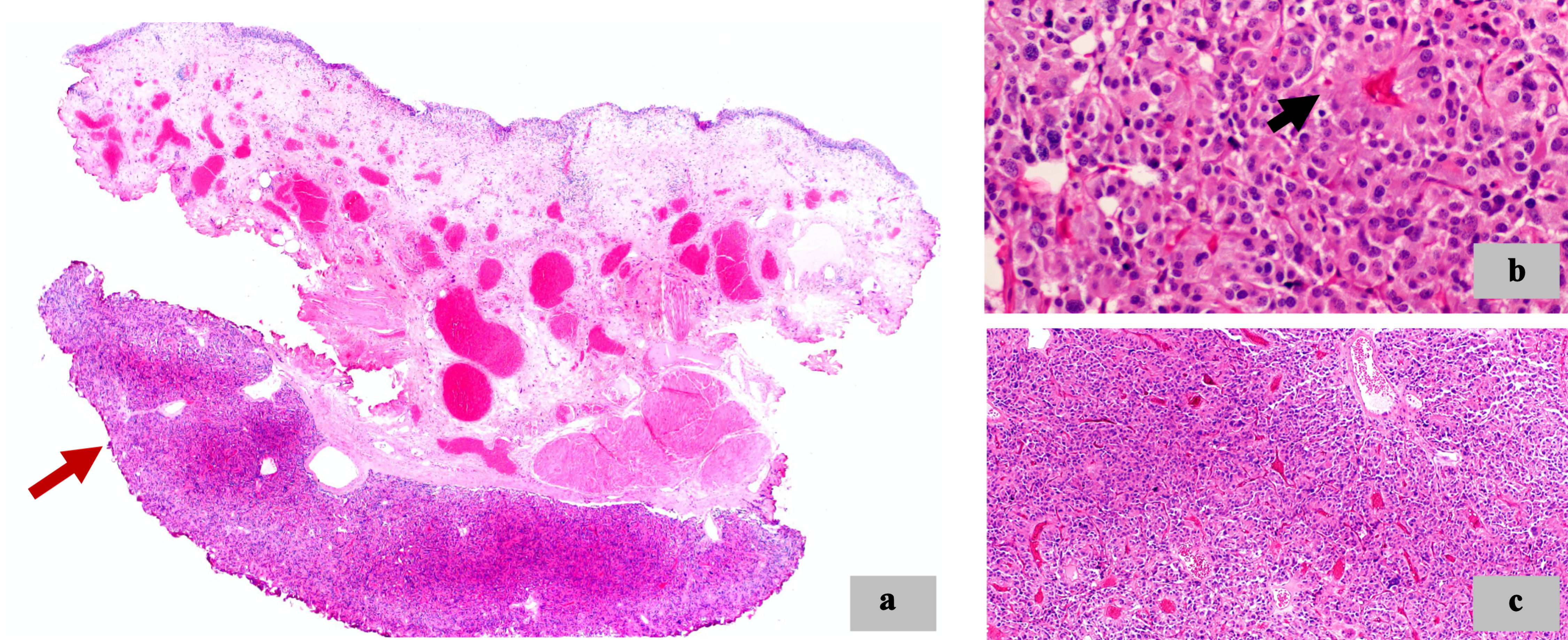
Figure 4. Morphologic features and immunohistochemistry techniques. (a) Neoplastic cells with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm, round to oval nuclei (× 20). (b) Synaptophysin (diffuse cytoplasmic staining) (× 20). (c) Chromogranin A (diffuse cytoplasmic staining) (× 20). (d) S100 highlights sustentacular cells (× 20). (e) SDHB immunoreactivity retained (× 20). (f) CKAE1/AE3 negative (× 20). SDHB: succinate dehydrogenase B; CKAE1/AE3: cytokeratin AE1/AE3.