Figures
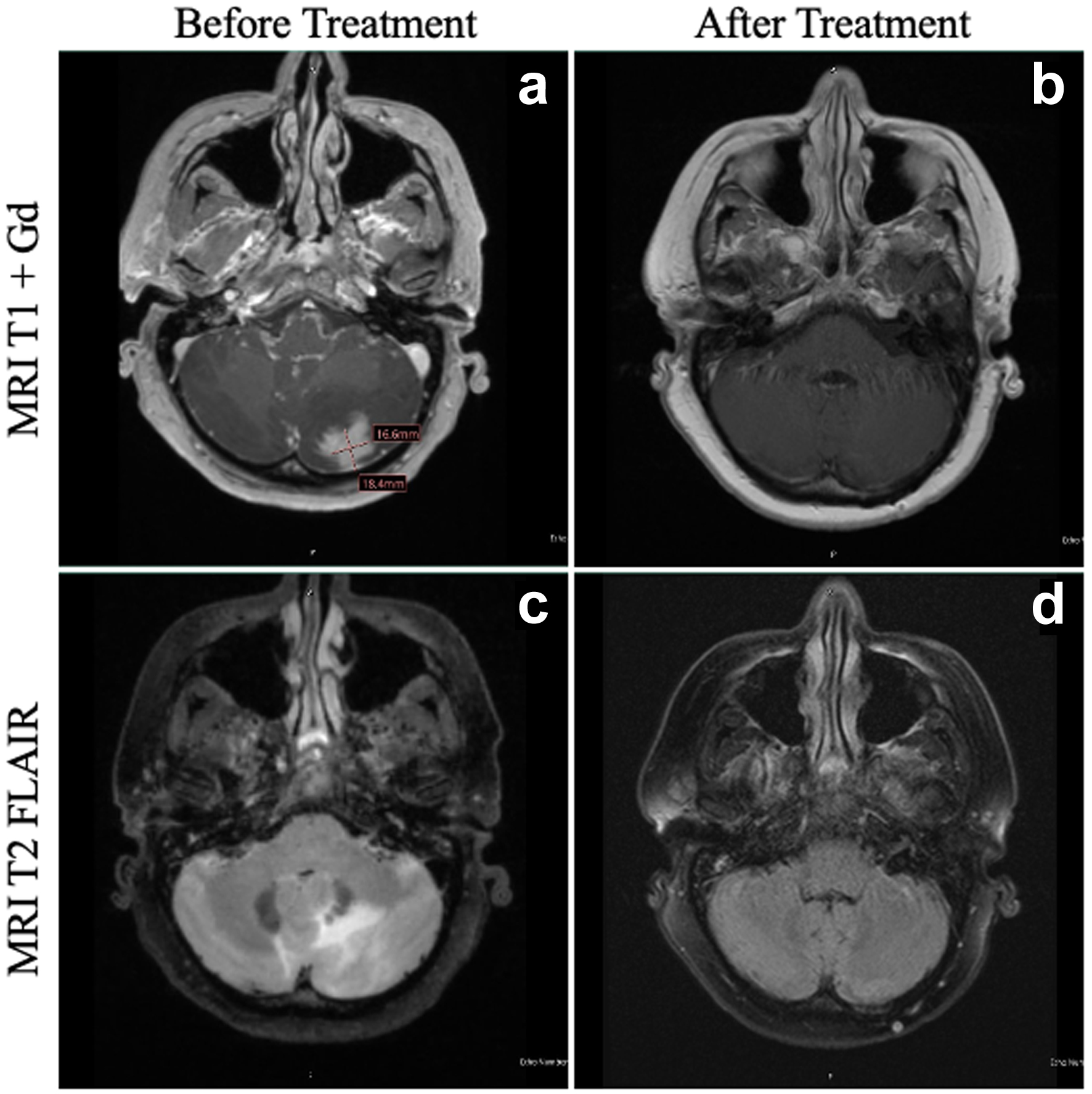
Figure 1. MRI of the patient’s brain before and after HDC-ASCT. At the time of diagnosis of PCNSTL, the patient had a lesion in the left cerebellum on T1 + Gd (a), with significant vasogenic edema evident on T2 FLAIR (c). At 1 year following HDC-ASCT, the patient has complete resolution of both the area of the primary cerebellar lesion (b) as well as total resolution of vasogenic edema (d). FLAIR: fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; HDC-ASCT: high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; PCNSTL: primary CNS T-cell lymphoma.
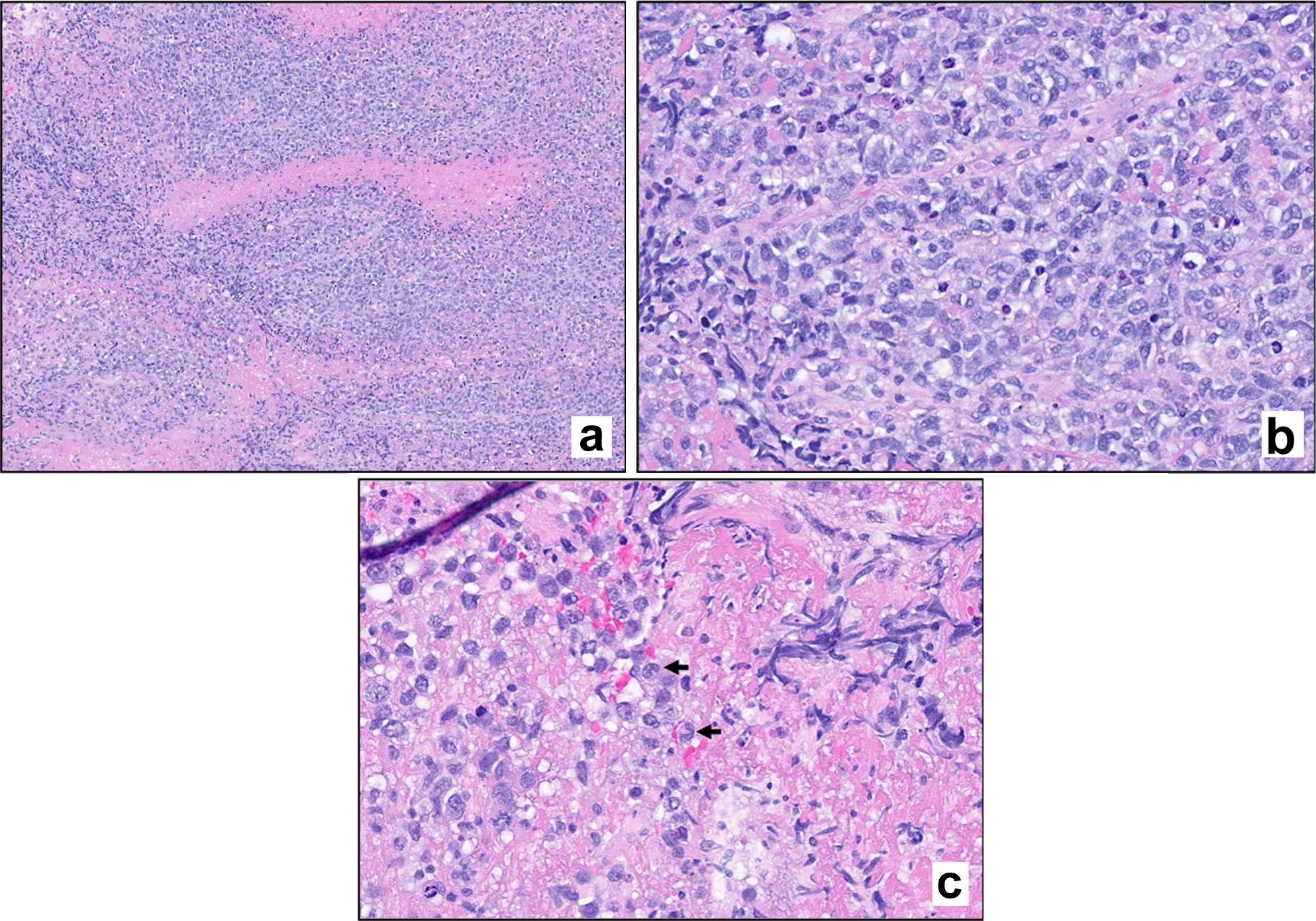
Figure 2. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain. Stained sections reveal fragments of brain parenchyma with a diffuse infiltrate of large atypical lymphoid cells. Mitotic figures are evident (a, × 100 magnification; b, × 400 magnification). Scattered cells exhibit morphologic features consistent with hallmark cells (c, arrows).
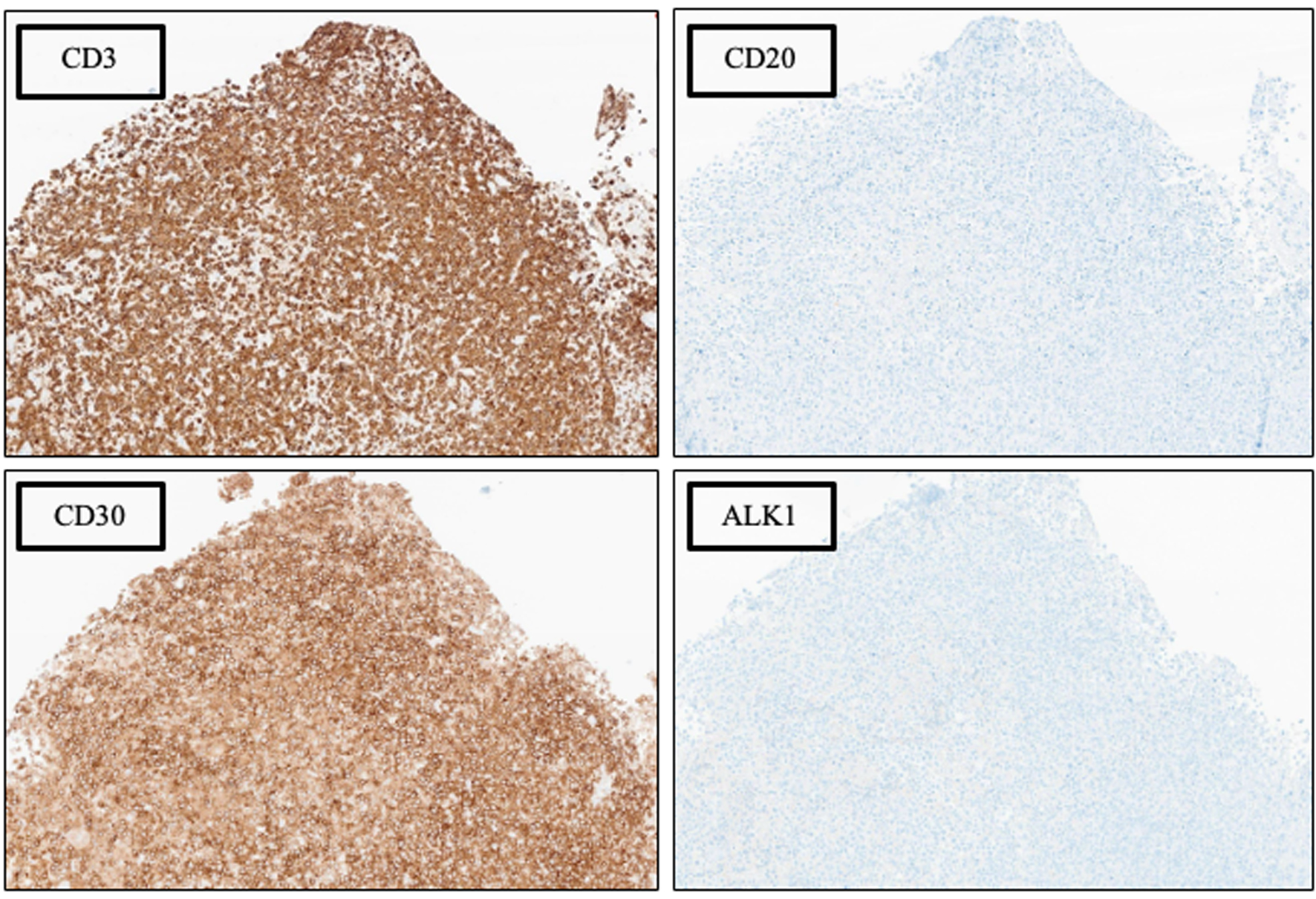
Figure 3. Phenotypic characterization by immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis, × 100 magnification. See Table 1 for additional IHC findings.
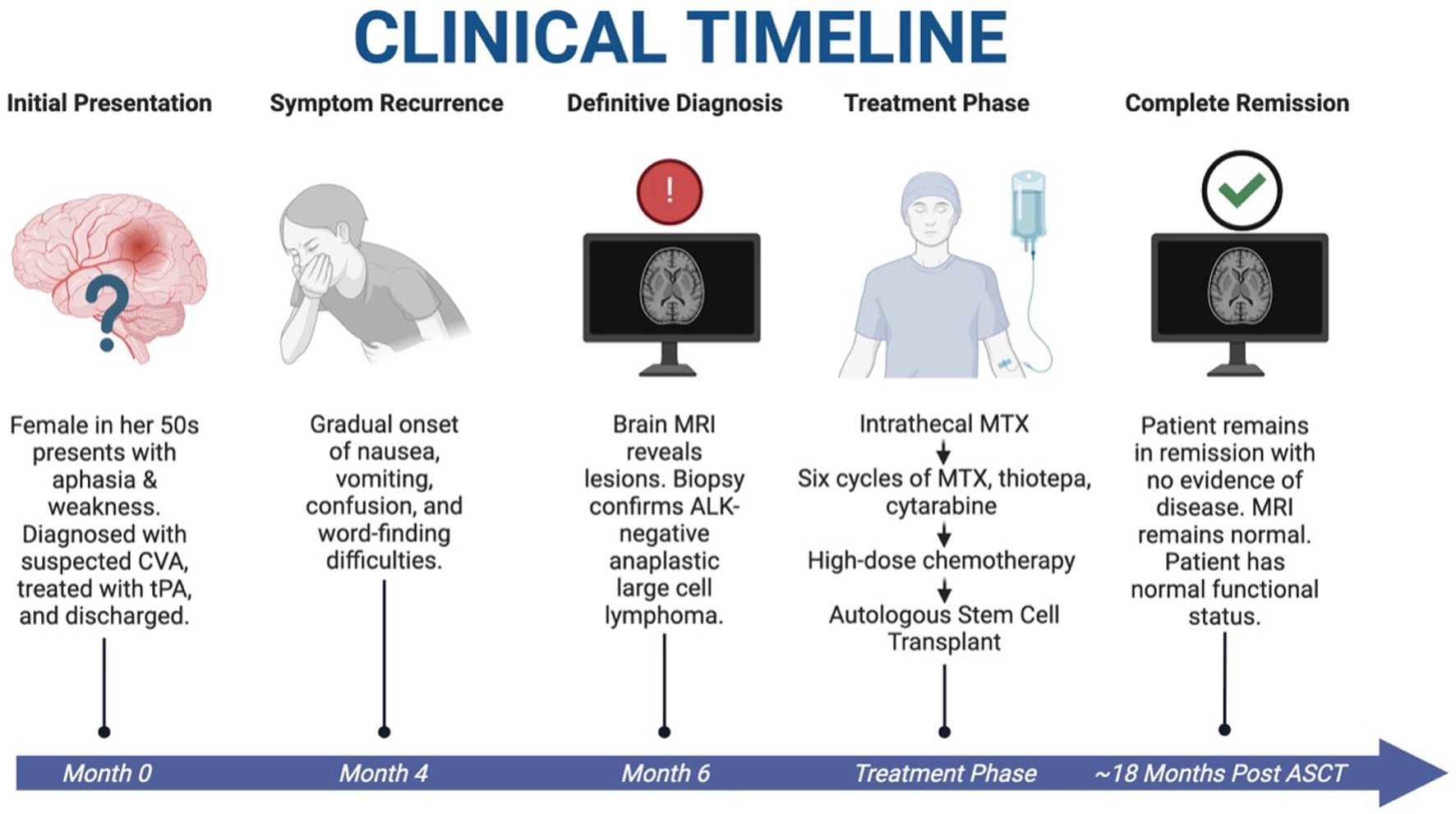
Figure 4. Clinical timeline of case. A patient with initial stroke-like symptoms was found to have PCNSTL. She underwent HDC-ASCT and is currently in complete remission with resolution of symptoms and restoration of normal functional status at approximately 18 months after HDC-ASCT. HDC-ASCT: high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation; PCNSTL: primary CNS T-cell lymphoma. Created in BioRender. Holley, N. (2025) https://BioRender.com/kdfox90.
Table
Table 1. Additional Immunohistochemical and in situ Hybridization Results
| Positive markers | Negative markers |
|---|
| EBER ISH: Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNA in situ hybridization. |
| CD2 (weak) | CD5 |
| CD4 (minor subset) | CD8 |
| CD7 | CD10 |
| CD43 | CD15 |
| CD56 (weak) | CD34 |
| Ki67 (> 95%) | CD138 |
| PD1 (subset) | EBER ISH |
| TIA1 | EMA |
| PAX5 |
| p63 |



