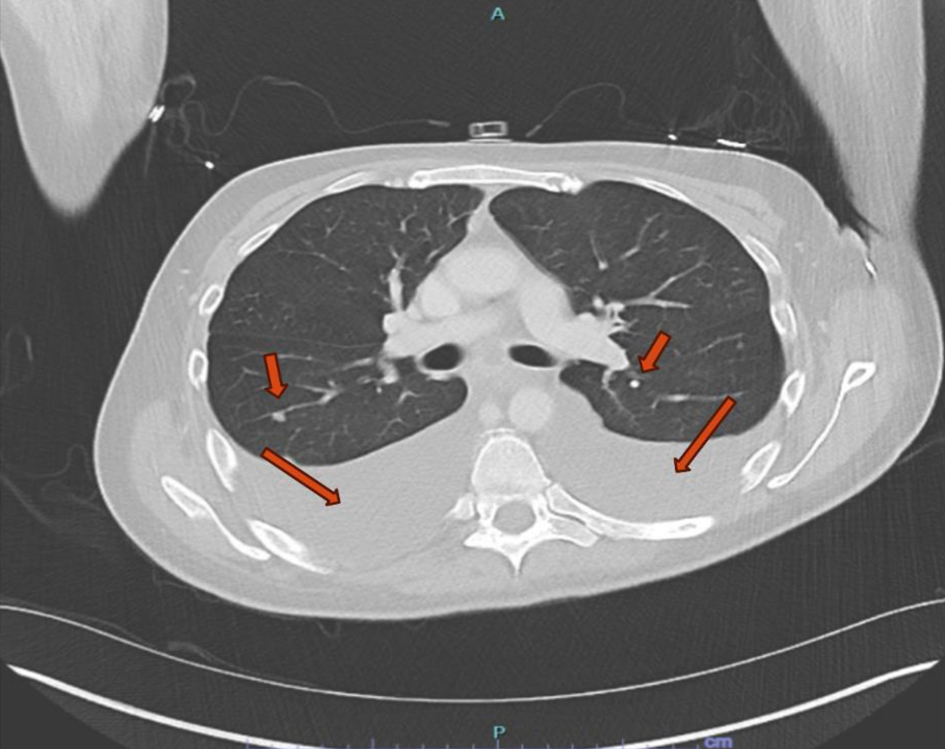
Figure 1. Computed tomography scan of the chest. Large bilateral pleural effusions with adjacent atelectasis and scattered pulmonary nodules (red arrows).
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://jmc.elmerpub.com |
Case Report
Volume 16, Number 4, April 2025, pages 146-152
Double Trouble in the Pericardium: A Rare Co-Infection of Tuberculosis and Tularemia Leading to Cardiac Tamponade
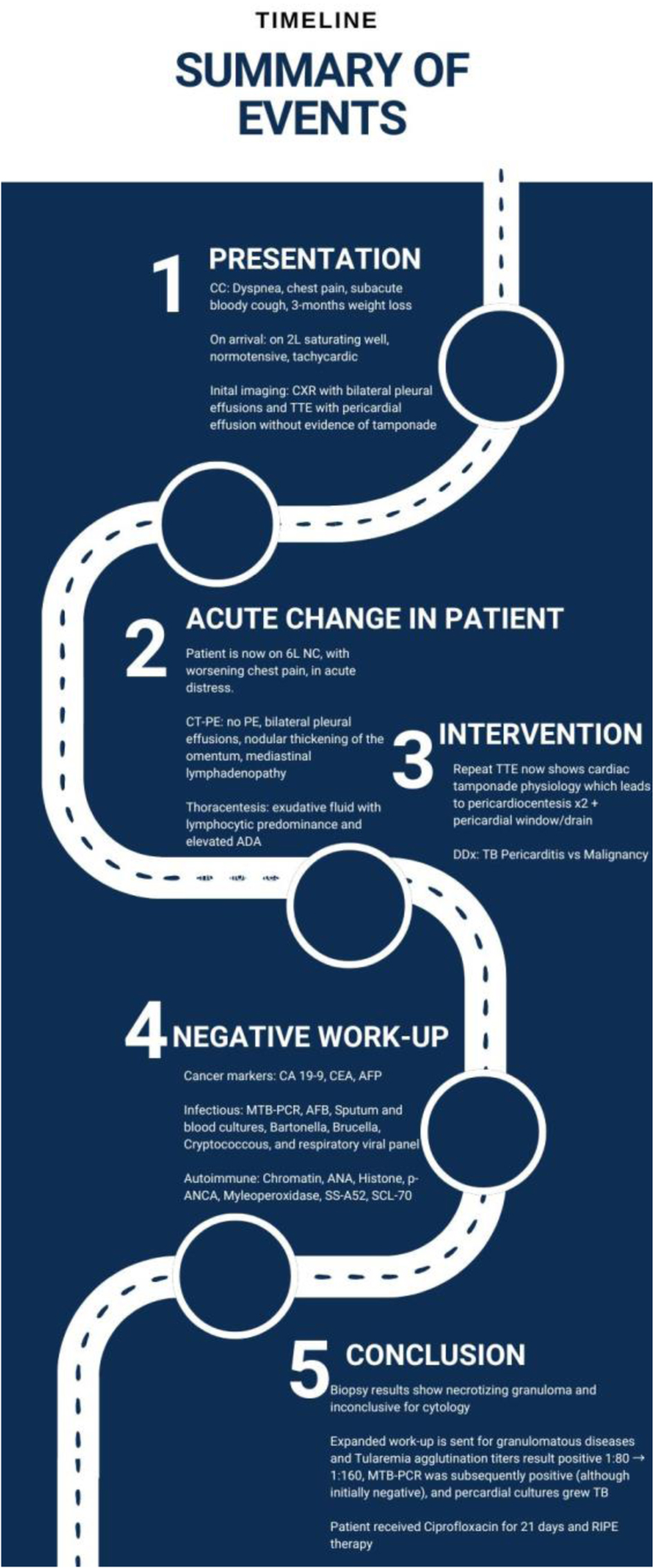
Figures

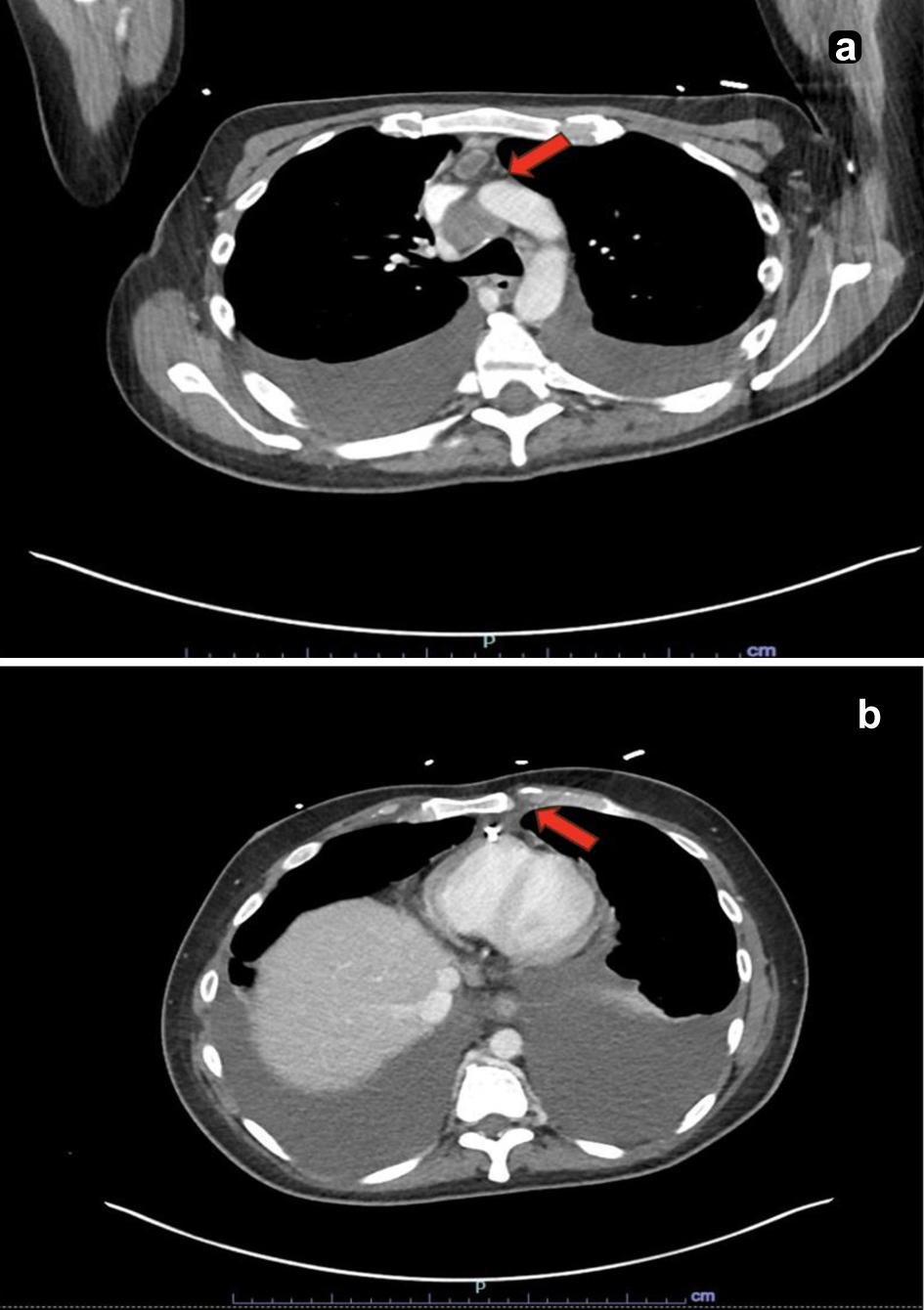
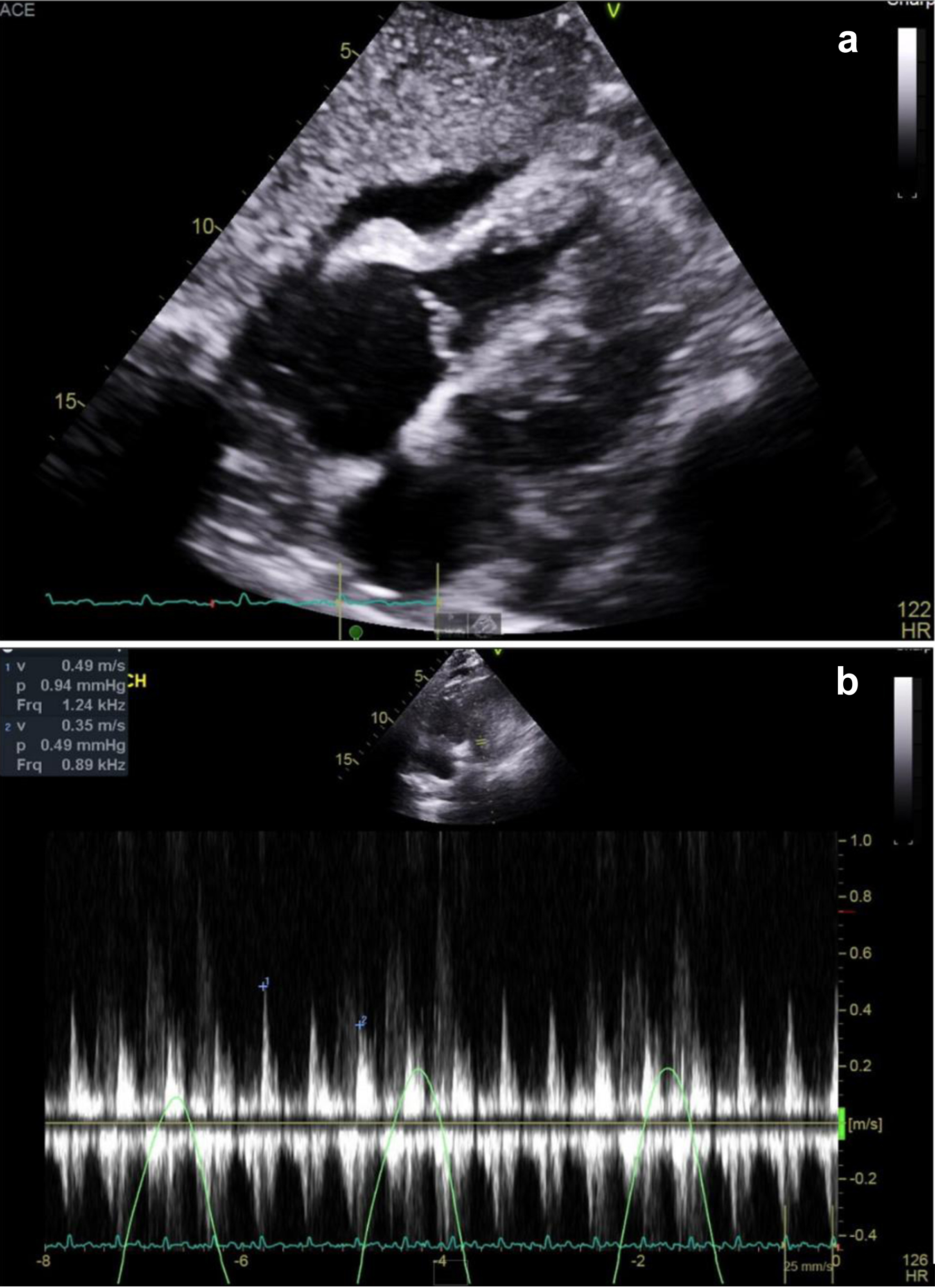
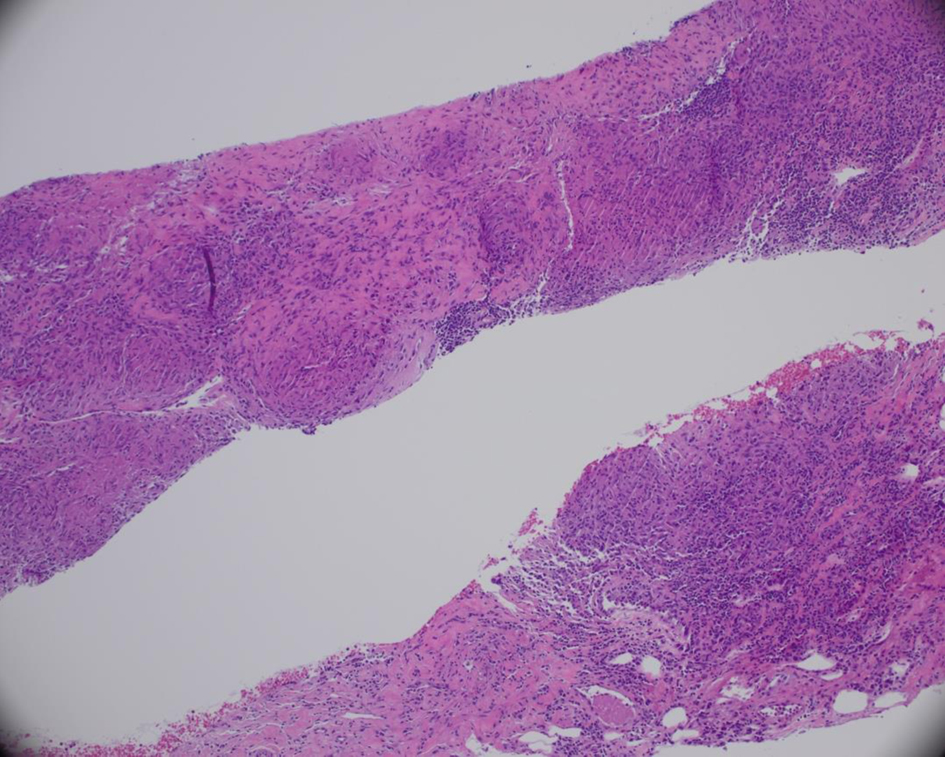
Table
| Category | Diagnoses |
|---|---|
| Infectious | Mycobacterial (Mycobacterium tuberculae, Mycobacterium leprae) Bacterial (Treponema pallidum, Bartonella henselae, Brucella, Francisella tularensis, Listeria monocytogenes, Chlamydia trachomatis, Nocardia) Fungal (Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides spp., Blastomyces dermatitidis, Cryptococcus neoformans) |
| Autoimmune and inflammatory | Sarcoidosis, Crohn disease, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, primary biliary cholangitis, Churg-Strauss syndrome |
| Malignancy | Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| Exposure induced | Beryllium and silicone exposure, hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
| Immunodeficiency | Chronic granulomatous disease |