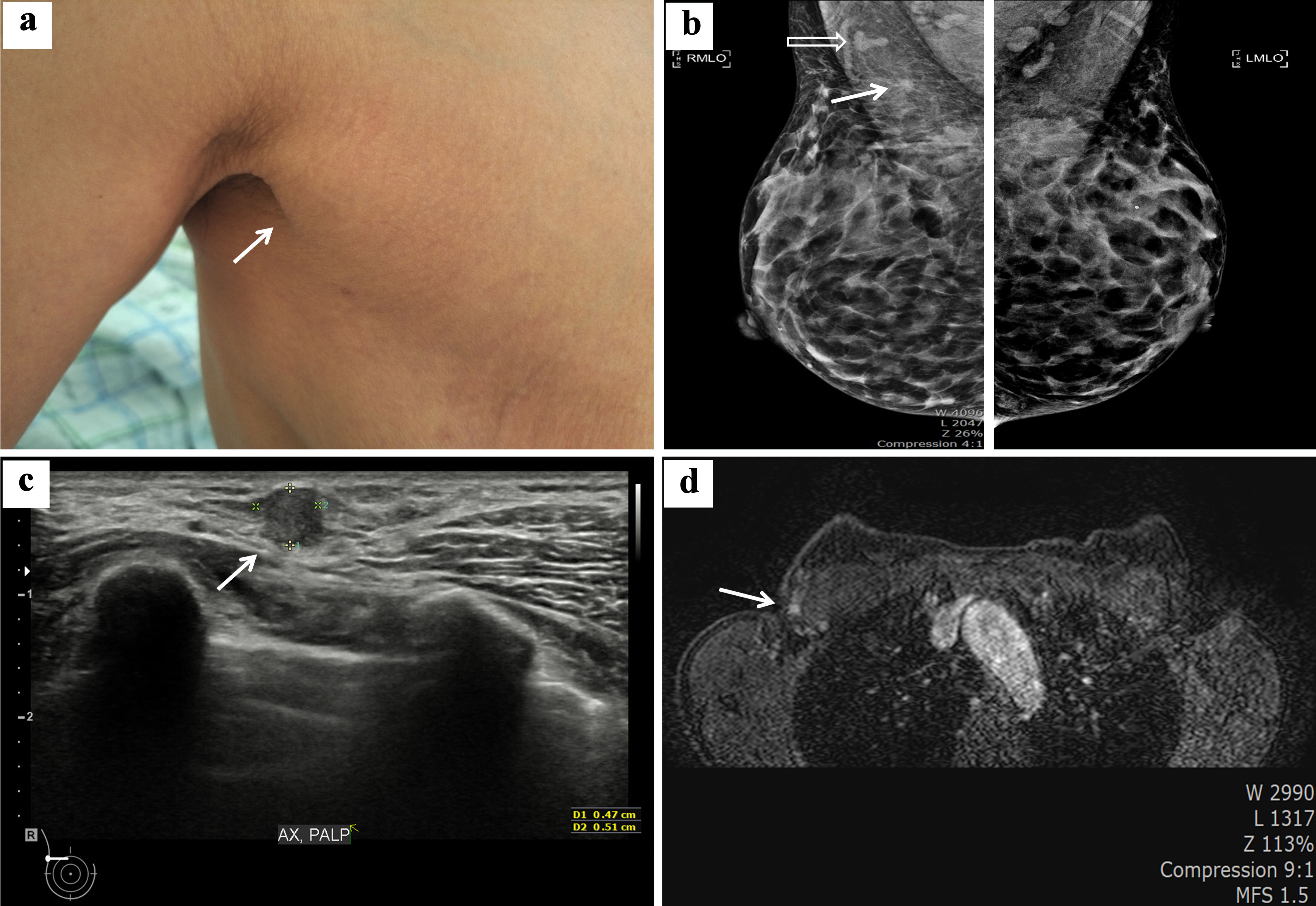
Figure 1. Clinical and radiologic findings of the right axilla mass diagnosed as invasive tubular carcinoma. (a) Exposed axilla shows right axillary swelling compatible with accessory breast (white arrow). (b) Mammographic image in the mediolateral oblique position revealing bilateral axillary accessory breast and demonstrating a 0.6 cm irregular asymmetric density (white arrow) and a suspicious lymph node (white nonshaded arrow) in the right axilla. (c) Breast ultrasonographic imaging shows a 0.51 × 0.47 cm irregular shaped hypoechoic mass located in the right axilla (white arrow). (d) Contrast- enhanced T1 breast magnetic resonance imaging shows a 0.6 cm, ill-defined enhancing nodule on the right axilla (white arrow).
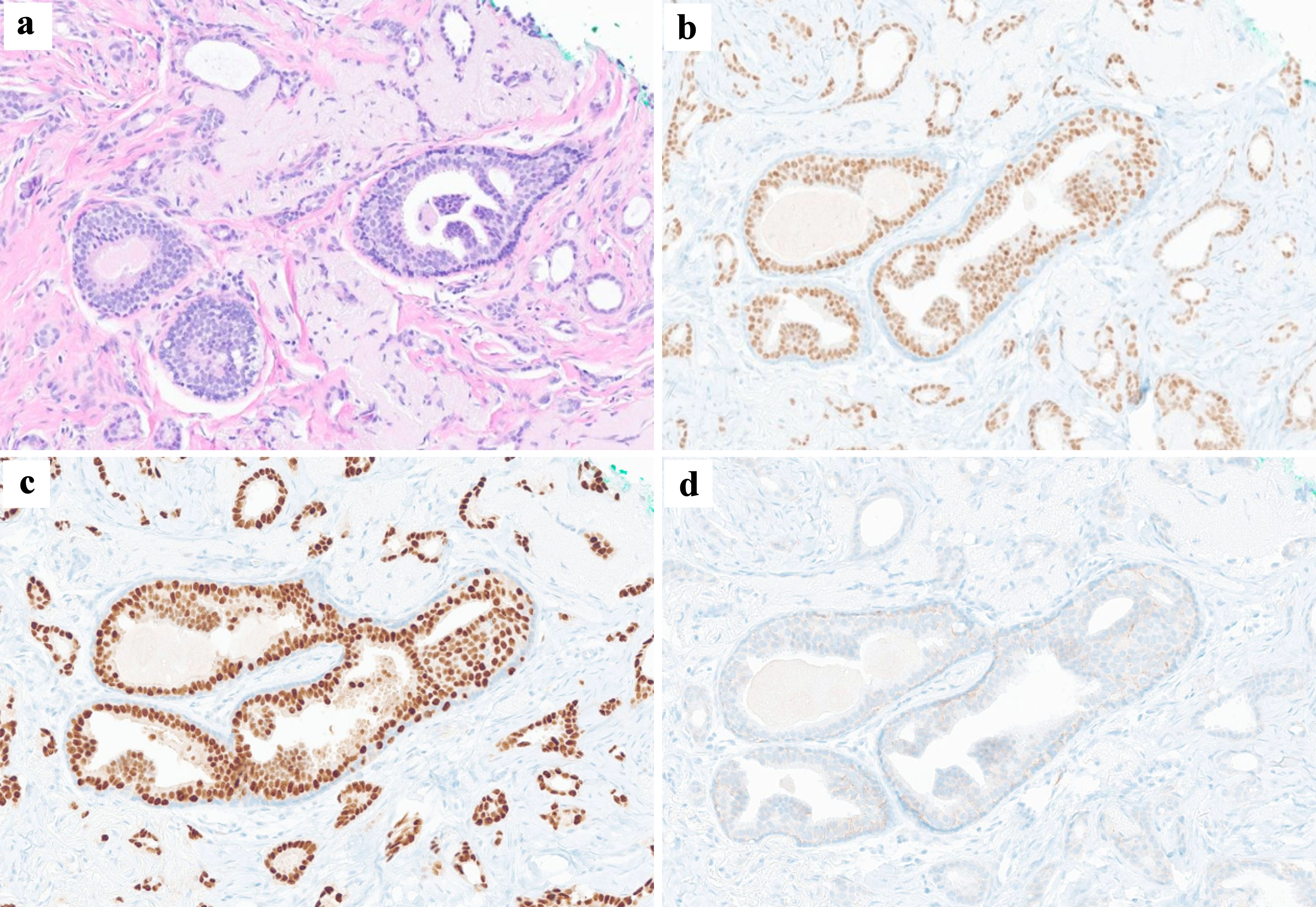
Figure 2. Histologic findings of core needle biopsy specimen. (a) Histopathology shows low-grade invasive ductal carcinoma with tubular pattern, with no marked pleomorphism of the nuclei (hematoxylin and eosin staining × 100). The primary breast carcinoma was immunohistochemically positive for estrogen receptor (b) and progesterone receptor (c) and negative for C-erb-B2 (d).
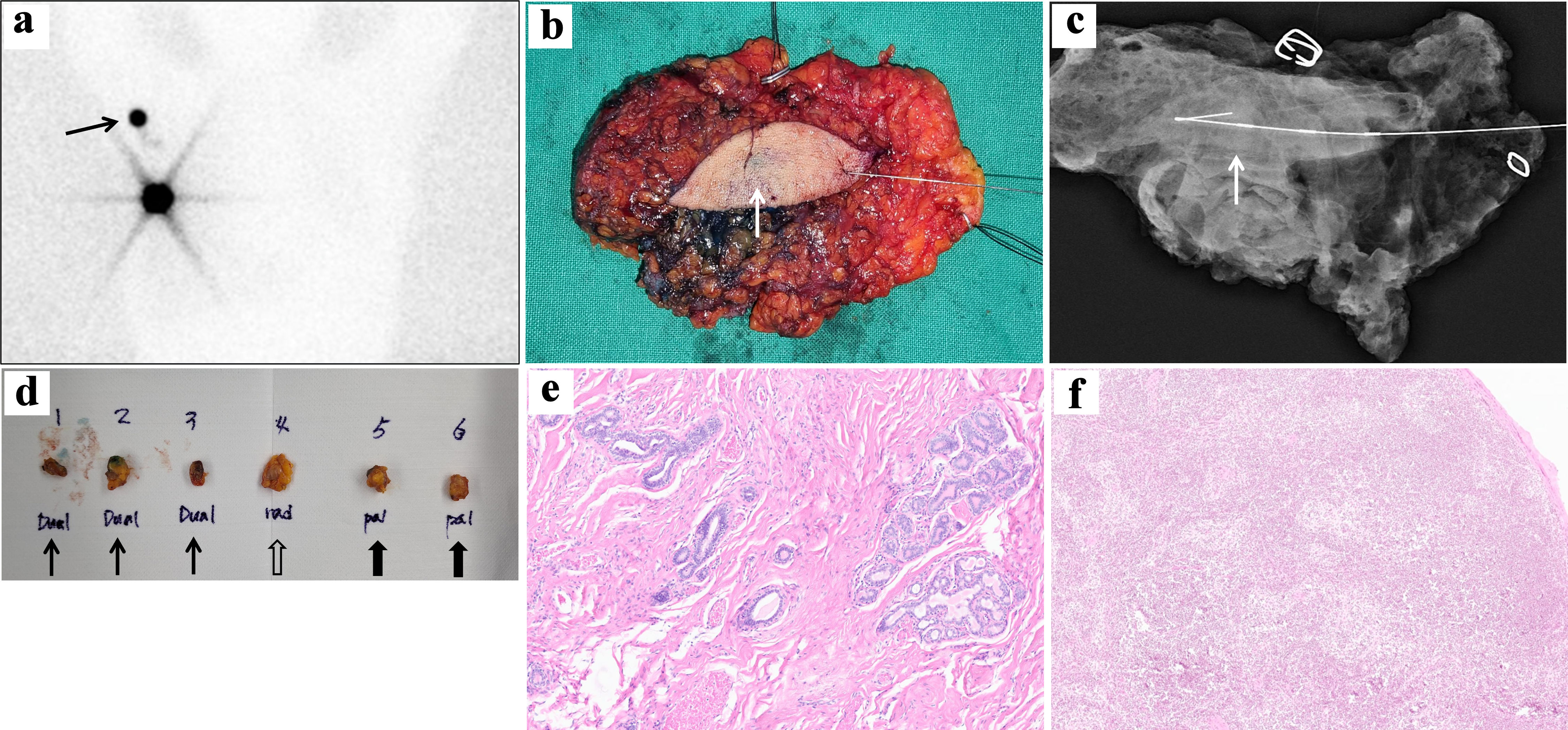
Figure 3. Operative procedures and findings of the patient. (a) Sixty minutes delayed image of preoperative lymphoscintigraphy after subareolar injection of 400 µCi technetium-99m sulfur colloid clearly visualizes right axillary sentinel lymph node (black arrow). (b) After intraoperative ultrasonography-guided wire localization of axilla mass, total excision of right axillary accessory breast including malignancy was performed. The intratumoral blue indigo-carmine injection is identified (white arrow). (c) Specimen mammography shows centrally located wire and poorly defined asymmetric density (white arrow). (d) Three dual tracer-uptake sentinel lymph nodes (black arrow) and one radioactive sentinel lymph node (black nonshaded arrow) were dissected through dual mapping with a subareolar radionuclide tracer and intratumoral indigo-carmine injections. Two additional palpable sentinel lymph nodes (black shaded arrow) were also dissected. (e) Histologic finding of breast carcinoma on breast conserving surgery (BCS) specimen showed low-grade invasive tubular carcinoma, with tubular growth in > 90% of tumor, with ovoid tubules with open lumina, with no marked pleomorphism of the nuclei and no increased mitotic activity (hematoxylin and eosin staining × 40). (f) Sentinel lymph node showed no evidence of metastasis (hematoxylin and eosin staining × 40).


