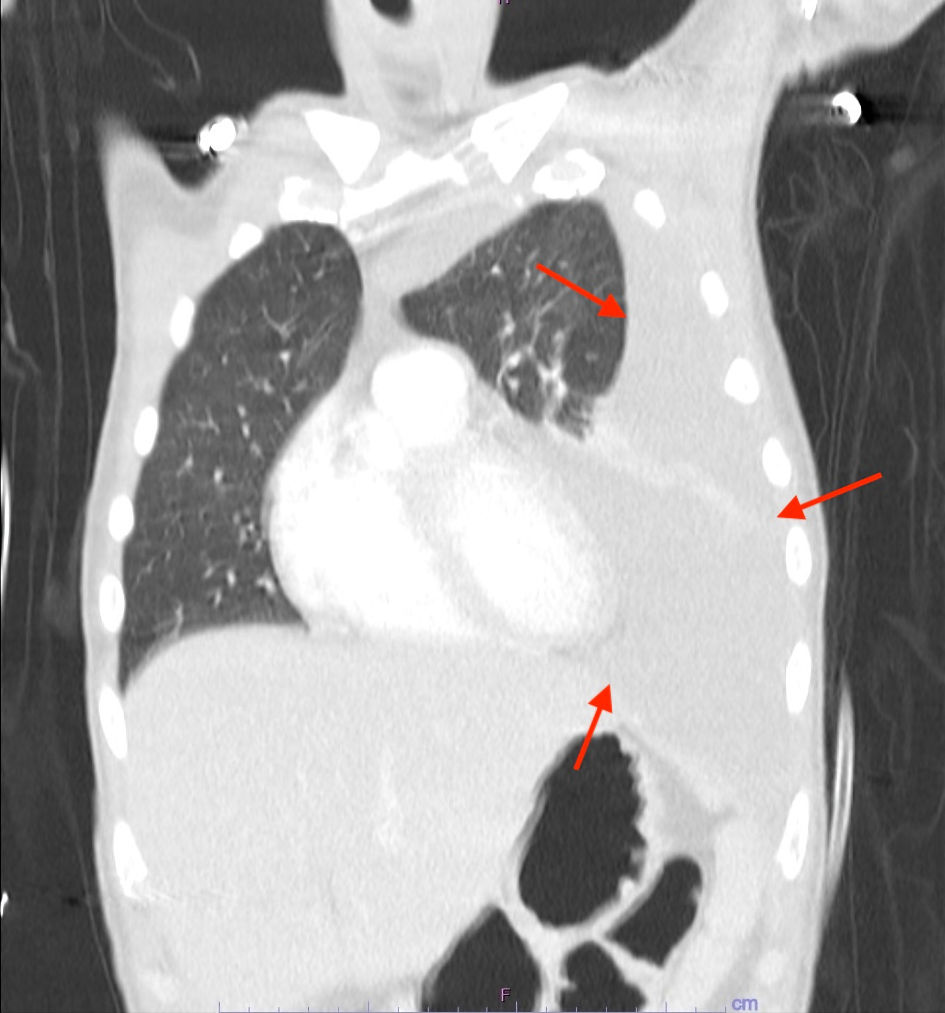
Figure 1. CT of the chest with contrast demonstrating an 8.7 × 7.1 × 4 soft tissue mass extending along the middle and posterior mediastinum into the left hilum (arrow). The lesion is exerting mass effect on the left atrium, encasing several pulmonary veins, and effacing the fat plane along the anterior esophagus with esophageal wall thickening. CT: computed tomography.
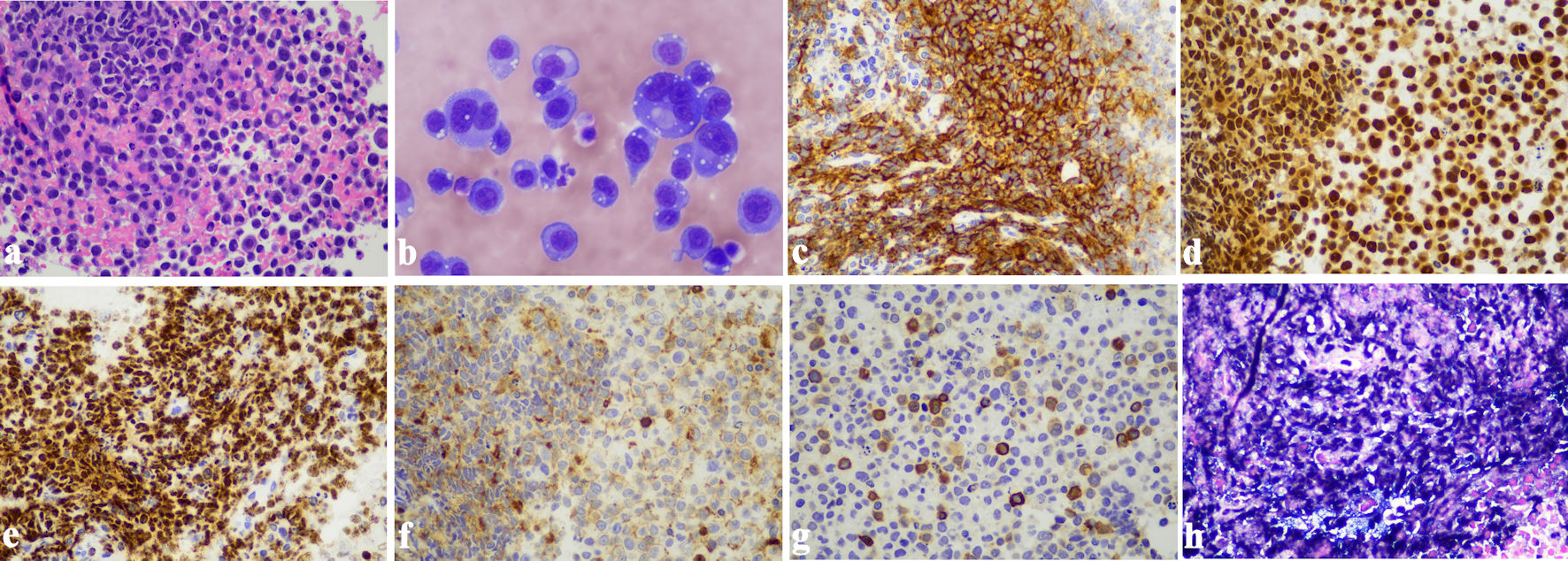
Figure 3. Primary effusion lymphoma. (a) Sheets of large pleomorphic lymphoma cells with prominent nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm, morphologically consistent with EC-PEL (H&E stain, original magnification: × 400). (b) Cytospin smear of pleural fluid showing PEL (Wright-Giemsa stain, original magnification: × 600). (c) Strong positive immunostaining for CD138 in neoplastic cells (immunohistochemistry, original magnification: × 400). (d) Strong positive immunostaining for MUM-1 in neoplastic cells (immunohistochemistry, original magnification: × 400). (e) The lymphoma cells demonstrate strong positive immunostaining for HHV8 (immunohistochemistry, original magnification: × 400). (f) Weak positive immunostaining for CD45 in neoplastic cells (immunohistochemistry, original magnification: × 400). (g) A small subset of neoplastic cells showed positive immunostaining for CD3 (immunohistochemistry, original magnification: × 400). (h) In situ hybridization for EBER was positive in the lymphoma cells (original magnification: × 400). EBER: Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNA; EC-PEL: extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma; H&E: hematoxylin and eosin stain; PEL: primary effusion lymphoma.