Hypophosphatemic Osteomalacia Induced by Low-Dose Adefovir-Related Fanconi Syndrome
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc5281Keywords:
Adefovir dipivoxil, Fanconi’s syndrome, Hypophosphatemic osteomalaciaAbstract
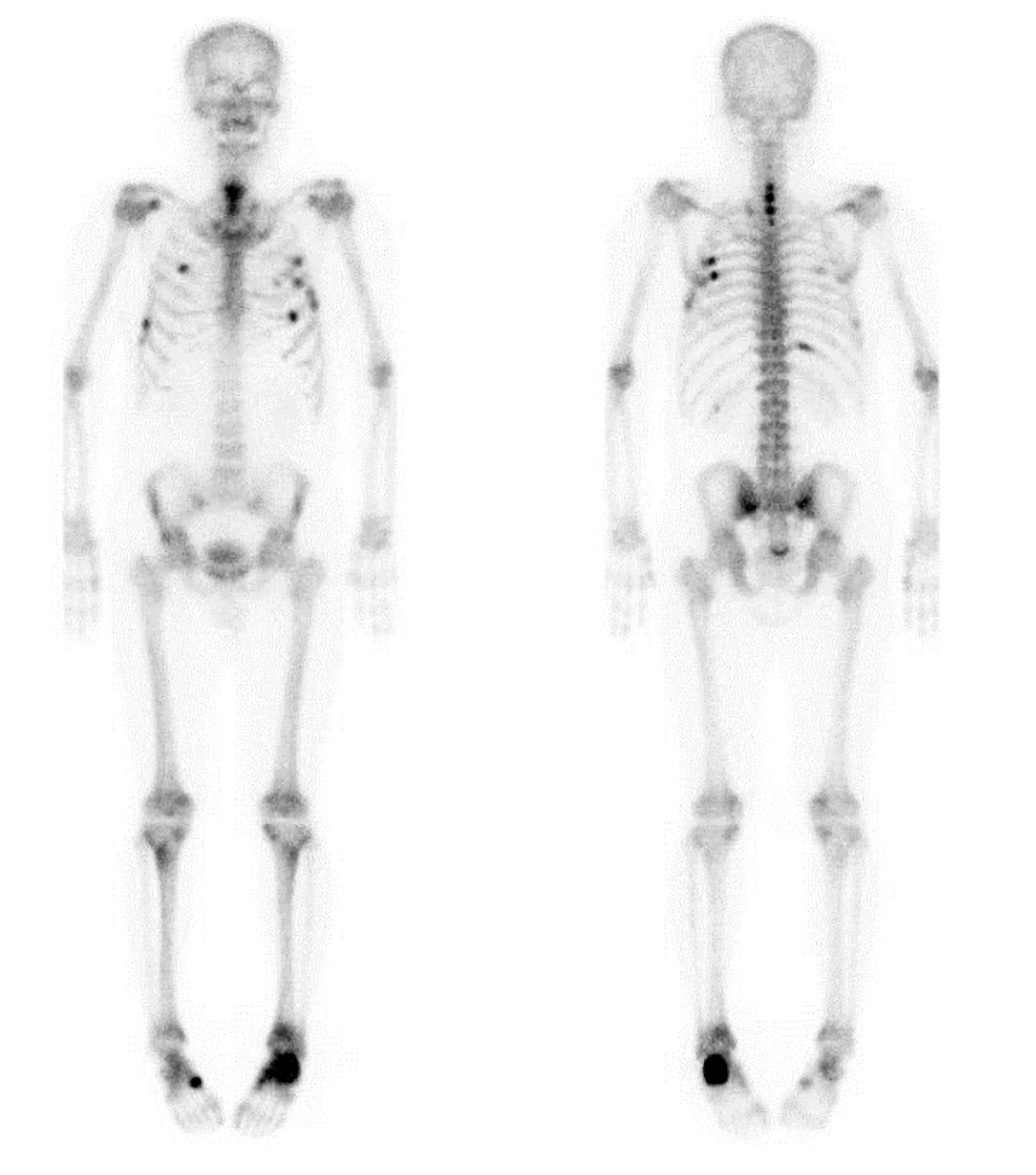
Adefovir dipivoxil (ADV), an antiviral agent for chronic hepatitis B virus infection, has been associated with nephrotoxicity, particularly Fanconi syndrome, even at low doses (10 mg/day). Fanconi syndrome is a generalized proximal tubular dysfunction leading to phosphate wasting and hypophosphatemic osteomalacia. Here, the author reports a case of a 58-year-old man with a 2-year history of bone pain involving the left foot, upper back, and left scapula, later extending to the right foot and chest wall, without antecedent trauma. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed insufficiency fractures in both calcanei and healing fractures of the spinous processes from the sixth cervical to the second thoracic vertebrae with callus formation. Whole-body bone scintigraphy demonstrated increased uptake in multiple ribs, the lower sacral region, and the aforementioned areas. Imaging findings, together with elevated serum alkaline phosphatase with increased bone fraction, prompted an extensive malignancy workup, which was negative. The patient had been taking ADV 10 mg daily for 10 years for chronic hepatitis B. Laboratory evaluation showed mild renal dysfunction, hypophosphatemia, hypouricemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase, proteinuria, phosphaturia, and glucosuria without hyperglycemia. He was diagnosed with hypophosphatemic osteomalacia secondary to ADV-induced Fanconi syndrome. After switching from ADV to entecavir and initiating supplementation with calcitriol and phosphate, the patient’s symptoms and laboratory abnormalities improved significantly. Careful monitoring of serum phosphate, alkaline phosphatase, and renal function is essential for early recognition and timely intervention in these potentially reversible adverse drug reactions.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









