Investigation and Management of a Small Outbreak of Septic Knee Arthritis Following Knee Arthroscopy by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc5138Keywords:
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Knee septic arthritis, Surgical site infection, Nosocomial infection, Arthroscopy, SterilizationAbstract
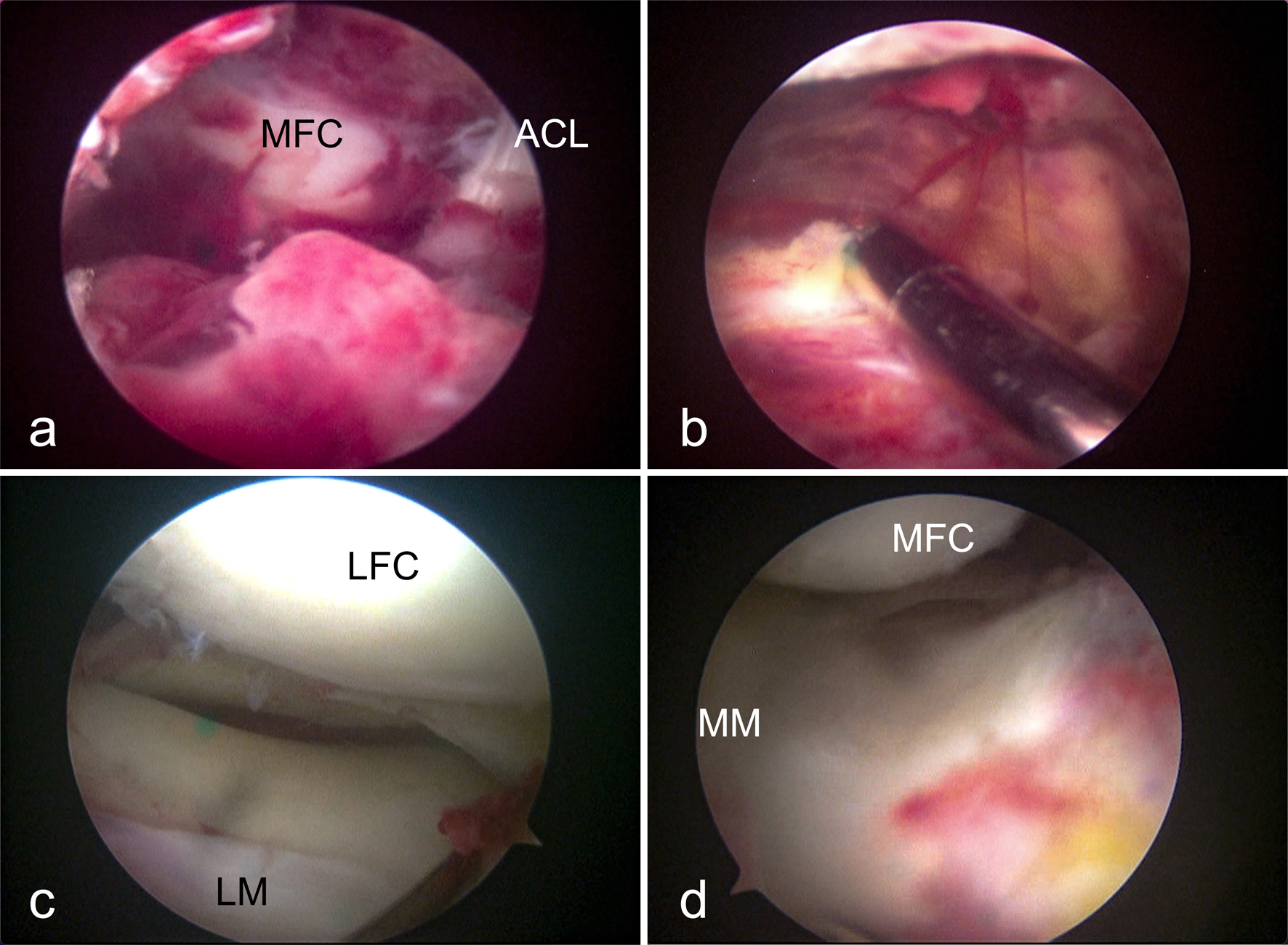
Knee septic arthritis caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (S. maltophilia) was very rare in immunocompetent group but was observed in a series of post-arthroscopy patients in our hospital. This study aimed to report the clinical course and treatments of the infections and the investigation of the incidents. One patient who underwent knee arthroscopy exhibited serious knee septic arthritis 17 days postoperatively. Later, three more similar patients were also suspected of knee infection. Investigation was initiated by interviews with personnel and reviews of medical records. All instruments associated with arthroscopy were subsequently sampled and tested. While no abnormalities were revealed in medical personnel and records, positive culture of S. maltophilia was found on one arthroscope, used in all four infected patients. No violations were found in sterilization processes. The contaminated arthroscope was proven loss of airtightness subsequently. For infection treatment, double or triple therapy of levofloxacin, sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, and minocycline was administered, with additional debridement performed in one patient. By retrospective survey, another three patients were suspected of infection out of the total 19 patients who underwent knee arthroscopy in last 4 weeks. After intervention, all involved patients recovered. Although S. maltophilia is a rare cause of knee septic arthritis, it can still occur and even lead to nosocomial outbreaks through instrument-related transmission. Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, levofloxacin, and minocycline remain the treatment of choice, despite the rising global resistance rates. Although hydrogen peroxide gas plasma sterilization serves as a fast and effective method for instrument sterilization in arthroscopy, maintaining good arthroscope condition and airtightness ensures success, which warrants periodic checks.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









